4
Separation of Glycopeptides from a
Peptide Mixture
The glycoproteins discussed here were each digested
with trypsin and used to test the affinity of the
ProSwift ConA-1S Affinity column for glycopeptides. The
separation of nonglycosylated peptides and glycopeptides
by the ProSwift ConA-1S Affinity column and reanalysis
of the collected fractions by reversed-phase chroma-
tography were automated in an off-line 2D mode. The
peptide fractions were collected in a 96-well plate using
the fraction collector function of the WPS-3000TBFC
Autosampler. The collected fractions were then loaded
to an Acclaim PA2 column for peptide mapping.
Ovalbumin and ribonuclease B have only one glycosyl-
ation site, so a small fraction of their tryptic peptides will
be bound to the ProSwift ConA-1S Affinity column. In
contrast, HRP’s multiple glycosylation sites, combined
with glycan microheterogeneity on each site, predict that
it will have a larger fraction of its tryptic peptides
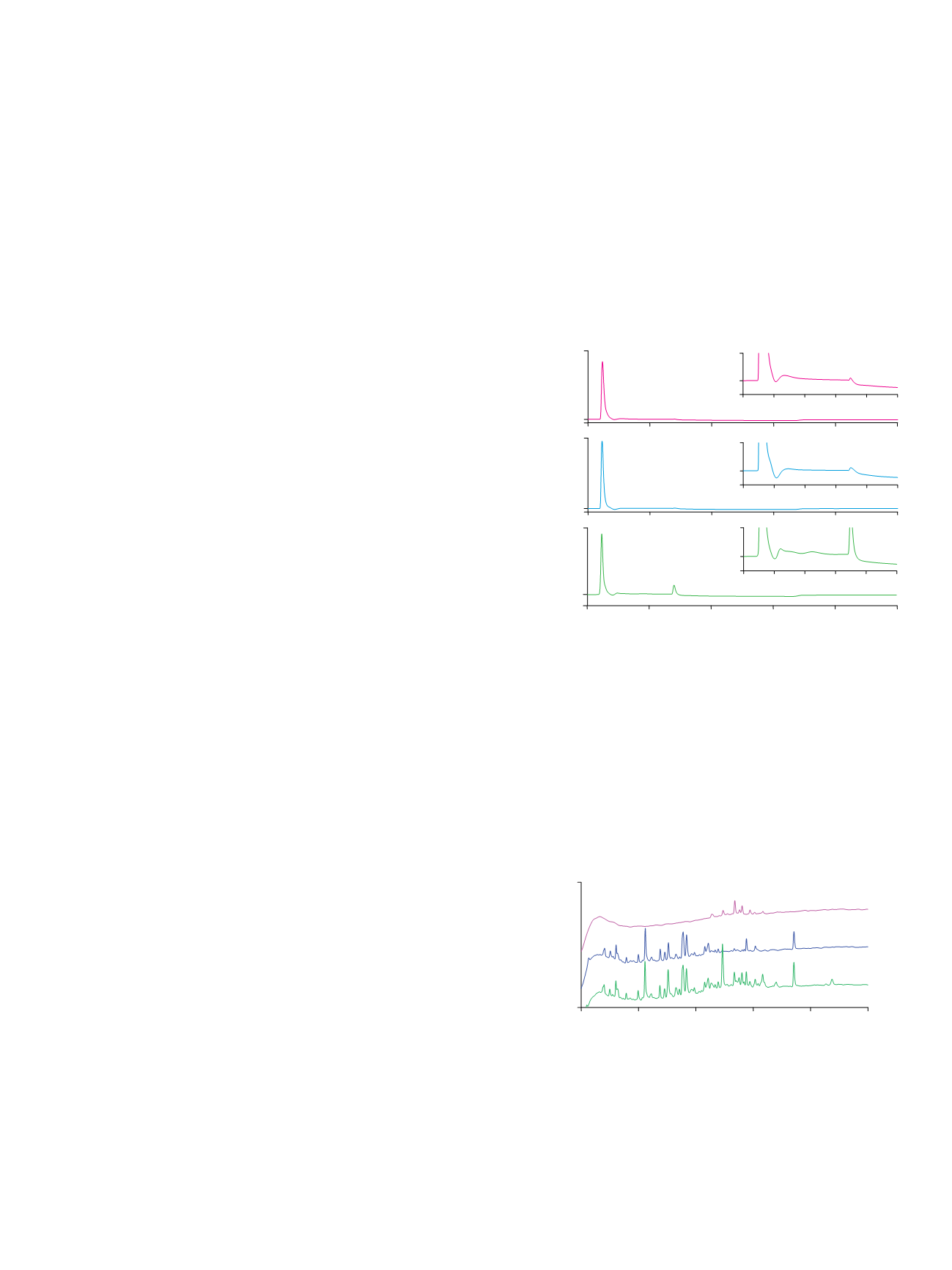
retained, which is confirmed in Figure 2C.
Figure 3 shows the peptide mapping of HRP tryptic
peptides, its Con A flow-through fraction (nonglycosylated
peptides), and its Con A captured fraction (glycopeptides).
The UV chromatogram of the glycopeptide fraction of
HRP digest shows approximately nine peaks, which may
correspond to its nine glycosylation sites. Attachment
of different glycans to the same glycosylation site (micro-
heterogeneity) will have minor effects on the retention
time of the peptide.
4
Therefore, a peptide with different
glycans attached may be shown as a single peak in a
reversed-phase chromatogram, albeit wider than a
nonglycosylated peptide.
Figure 2. Glycosylated tryptic peptides enrichment on the ProSwift ConA-1S
Affinity column.
Figure 3. Peptide mapping of (A) HRP tryptic peptides, (B) HRP tryptic peptides
ProSwift ConA-1S Affinity column flow-through fraction, and (C) HRP tryptic
peptides ProSwift ConA-1S Affinity column eluted fraction.
1
2000
mAU
-100
-200
1200
0
5
10
15
20
25
mAU
Minutes
2000
-100
mAU
Column:
ProSwift ConA-1S Affinity (5 × 50 mm)
Mobile Phase:
A: 50 mM sodium acetate, 200 mM sodium chloride, 1 mM calcium
chloride, pH 5.3
B: 100 mM
α
-methyl mannoside in mobile phase A
Gradient:
0–5.0 min, 0% B; 5.0–5.5 min,
0–100% B; 5.5–15 min, 100% B
Flow Rate:
0.5 mL/min
Inj. Volume:
20 µL
Temperature:
30 °C
Detection:
UV at 214 nm
Samples:
A
. Ovalbumin tryptic peptides
B
. Ribonuclease B tryptic peptides
C
. HRP tryptic peptides
Sample Preparation: Tryptic peptide samples diluted with mobile phase A,
1 mg/mL solution
Peaks:
1. Nonretained peptides
2. Retained peptides (nominally glycosylated)
3., 4. Peptides with weak interaction with Con A
0
2
4
6
Minutes
8
10
0
2
4
6
8
10
0
2
4
6
8
10
-50
mAU
100
-50
mAU
100
-50
mAU
100
Minutes
Minutes
The insets are enlargements of the first 10 min of each separation
1
2
3
C
1
2
3
4
1
2
1
2
3
A
2
B
1
2
160
-20
mAU
10
15
20
25
30
35
C
A
B
Minutes
Column:
Acclaim PA2, 3 µm (3.0 × 150 mm)
Mobile Phase:
A: Water with 0.05% formic acid
B: Acetonitrile with 0.04% formic acid
Gradient:
0–5.0 min, 0% B; 5.0–35.0 min,
0–50% B; 35.5–45.0 min, 90% B
Flow Rate:
0.425 mL/min
Inj. Volume:
20 µL
Temperature:
30 °C
Detection:
UV at 214 nm
Sample Preparation: HRP tryptic peptides diluted with mobile phase A,1 mg/mL solution


