2
Improving Intact Antibody Characterization by Orbitrap Mass Spectrometry
Instrument
A Thermo Scientific™ Surveyor
Orbitrap Elite mass spectromet
Samples were purified on a The
x 1 mm, 5 µm particles), solvent
0.1 % FA in ACN. The LC gradi
at a flow rate of 100 µL/min.
Data analysis was done using
packages.
Results
The analysis of large proteins
using Orbitrap mass spectrome
past few years. Large molecul
life-times due to their relatively
for intact antibodies is to us
available on the Orbitrap Elite
Introduction
Recombinant monoclonal antibodies have gained significant importance in
diagnostic and therapeutic applications over the past years. In order to verify
the correctness of the overall molecule to provide a reproducible, safe and
effective biological drug compound, the correct protein sequence, as well as
the presence and relative abundance of different glycoforms have to be
confirmed.
Here we present an approach to analyze an intact monoclonal antibody in
non-reduced and reduced condition by LC-MS using the Thermo Scientific™
Orbitrap Elite™ mass spectrometer. The intact antibody and the separated
light and heavy chains were analyzed in Full MS experiments as well as with
top-down experiments using in-source CID (SID), CID, HCD and ETD
fragmentation techniques making use of the ultrahigh resolution of the mass
spectrometer. For data evaluation ProSight software and Thermo Scientific™
Protein Deconvolution™ software version 1.0 packages were used.
Methods
Sample Preparation
AbbVie™ HUMIRA
™
(adalimumab, Figure 2) [1]: The intact antibody (144
kDa) was dissolved in 0.1 % FA to 1 µg/µL; 5 µg HUMIRA were loaded onto
the column.
For analyzing HUMIRA light chain (24 kDa) and heavy chain (51 kDa)
separately, 50 µg HUMIRA was reduced with DTT (20-fold molar excess,
56°C for 1 h) and alkylated with iodoacetamide (50-fold molar excess, room
temperature for 30 min in the dark).
N-‐terminal heterogeneity
Pyroglutamateforma.on
Othermodifica.ons
Amino acid modifica4ons
Deamidataion,oxida.on,
glycosyla.on,isomeriza.on
Fragmenta4on
Cleavageinhingeregion
Oligosaccharides
Fucosyla.on,sialyla.on,galactosyla.on,...
Disulfide Bonds
Freethiols,disulfideshuffling,thioether
C-‐terminal heterogeneity
Lysineprocessing,Prolineamida.on
Heavy chain
C
H
3
C
H
2
-‐S-‐S-‐
-‐S-‐S-‐
S S
S S
Fab
Fc
-‐COO
-‐
Biological Characteris4cs
Physicochemical Characteris4cs
FIGURE 2:
3D structure of HUMIRA highlighting the attached glycans and
cystein residues forming inter- and intra-chain disulfide bridges.
FIGURE 4:
(A) Full MS spectr
zoom into the three most abund
after deconvolution.
(A)
(B)
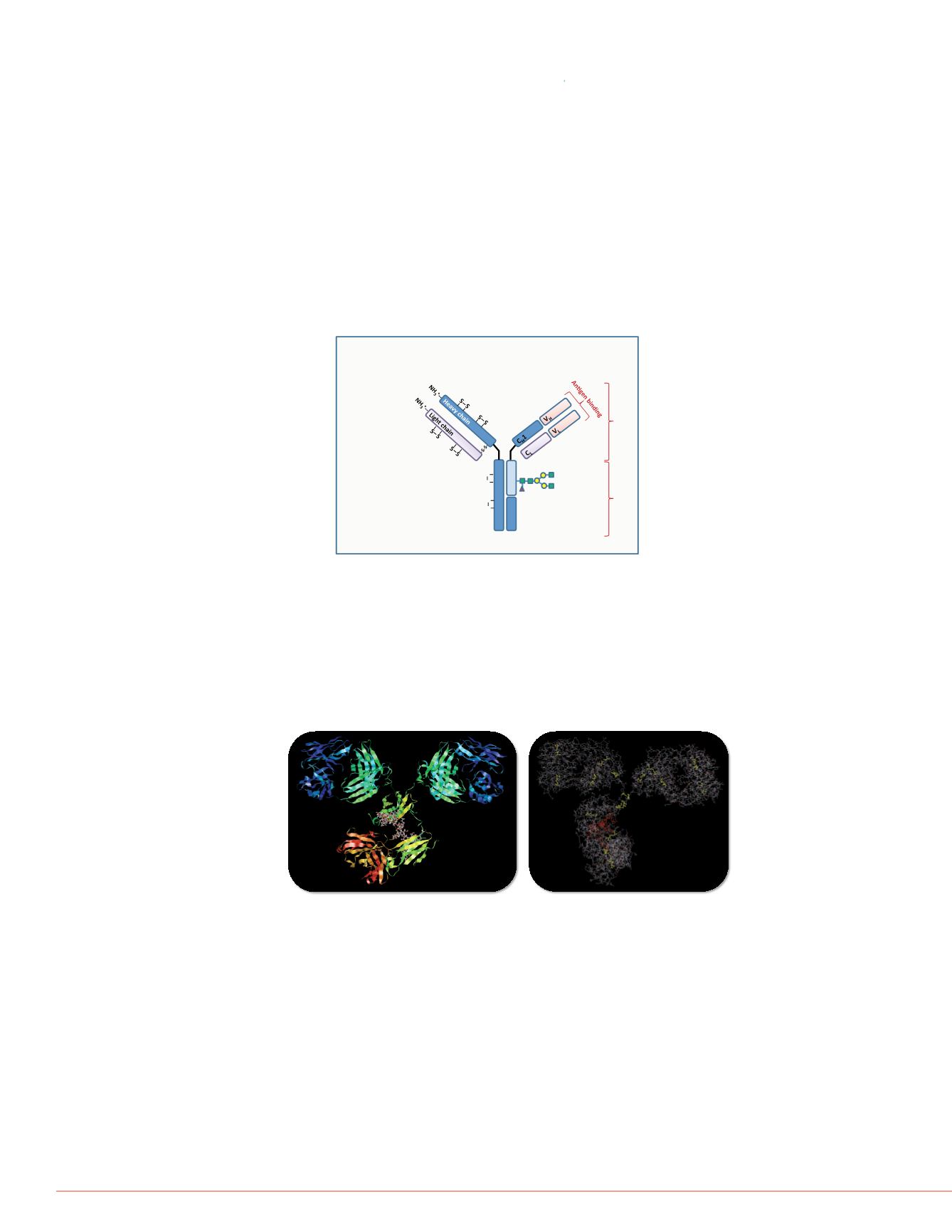
FIGURE 1:
General structure of mAbs and their biological and
physico-chemical characteristics
.
FIGURE 3:
Schematics of the
spectrometer equipped with an
Electrospraysource
S-lens
SquareQuadrupole
withBeamBlocker
Octopole
HighPressureCell
LowPres
2000
2500
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
Relative Abundance
27
2693.382
2598.92826
2510.86531
2428.59194
2351.52066
2279.19708
2178.67441
2029.53882


