Elemental compositions
C
H
N
O
S
MW
(monoisotopic)
MW
(average)
Light chain (LC) full sequence aa 1-213
1016
1577 273 328
6 23,042.34369 23,056.5
N-terminal pyro Glutamic acid
1016
1574 272 328
6 23,025.31714 23,039.4
N-terminal pyro Glutamic acid, 2 intrachain S-S bonds
1016
1570 272 328
6 23,021.28584 23,035.4
2 x LC (N-term. pyroGlu)
2032
3148 544 656 12 46,050.63428 46,078.9
2 x LC (N-term. pyroGlu, 2 intrachain S-S bonds each)
2032
3140 544 656 12 46,042.57168 46,070.8
Heavy chain (HC) full sequence aa 1-451
2197
3389 577 676 16 49,183.40813 49,214.0
N-terminal pyro Glutamic acid
2197
3386 576 676 16 49,166.38158 49,197.0
minus C-term. K (aa 1-450)
2191
3374 574 675 16 49,038.28661 49,068.8
minus 4 intrachain S-S bonds
2191
3366 574 675 16 49,030.22401 49,060.8
HC-G0F (pyro-Glu, - K, fully reduced)
2247
3466 578 714 16 50,482.82048 50,514.2
HC-G1F (pyro-Glu, - K, fully reduced)
2253
3476 578 719 16 50,644.87330 50,676.3
HC-G2F (pyro-Glu, - K, fully reduced)
2259
3486 578 724 16 50,806.92613 50,838.5
HC minus 4 intrachain S-S bonds + G0F
2247
3458 578 714 16 50,474.75788 50,506.1
2 x HC (pyroGlu, - K)
4382
6748 1148 1350 32 98,076.57323 98,137.7
2 x HC (pyroGlu, - K, 4 intrachain S-S bonds each)
4382
6732 1148 1350 32 98,060.44803 98,121.6
Man5 (HexNAc)2 (Hex)5
46
76
2
35
0
1216.42286
1217.1
G0 (HexNAc)4 (Hex)3
50
82
4
35
0
1298.47596
1299.2
G0F (HexNAc)4 (Hex)3 Fuc
56
92
4
39
0
1444.53387
1445.3
G1 (HexNAc)4 (Hex)4
56
92
4
40
0
1460.52878
1461.3
G1F (HexNAc)4 (Hex)4 Fuc
62
102
4
44
0
1606.58669
1607.5
G2 (HexNAc)4 (Hex)5
62
102
4
45
0
1622.58161
1623.5
G2F (HexNAc)4 (Hex)5 Fuc
68
112
4
49
0
1768.63951
1769.6
G1FSA (HexNAc)4 (Hex)4 Fuc SA
73
119
5
52
0
1897.68211
1898.7
G1FSA2
(HexNAc)4 (Hex)4 Fuc (SA)2
84
136
6
60
0
2188.77752
2190.0
G2FSA (HexNAc)4 (Hex)5 Fuc SA
79
129
5
57
0
2059.73493
2060.9
G2FSA2 (HexNAc)4 (Hex)5 Fuc (SA)2
90
146
6
65
0
2350.83035
2352.1
Man5/Man5 (HexNAc)4 (Hex)10
92
152
4
70
0
2432.84572
2434.2
G0F/G0F (HexNAc)8 (Hex)6 (Fuc)2
112
184
8
78
0
2889.06774
2890.7
G0F/G1F (HexNAc)8 (Hex)7 (Fuc)2
118
194
8
83
0
3051.12056
3052.8
G1F/G1F (HexNAc)8 (Hex)8 (Fuc)2
124
204
8
88
0
3213.17338
3215.0
G1F/G2F (HexNAc)8 (Hex)9 (Fuc)2
130
214
8
93
0
3375.22621
3377.1
G2F/G2F (HexNAc)8 (Hex)10 (Fuc)2
136
224
8
98
0
3537.27903
3539.2
G1F/G2FSA (HexNAc)8 (Hex)9 (Fuc)2 SA
141
231
9
101
0
3666.32162
3668.3
6
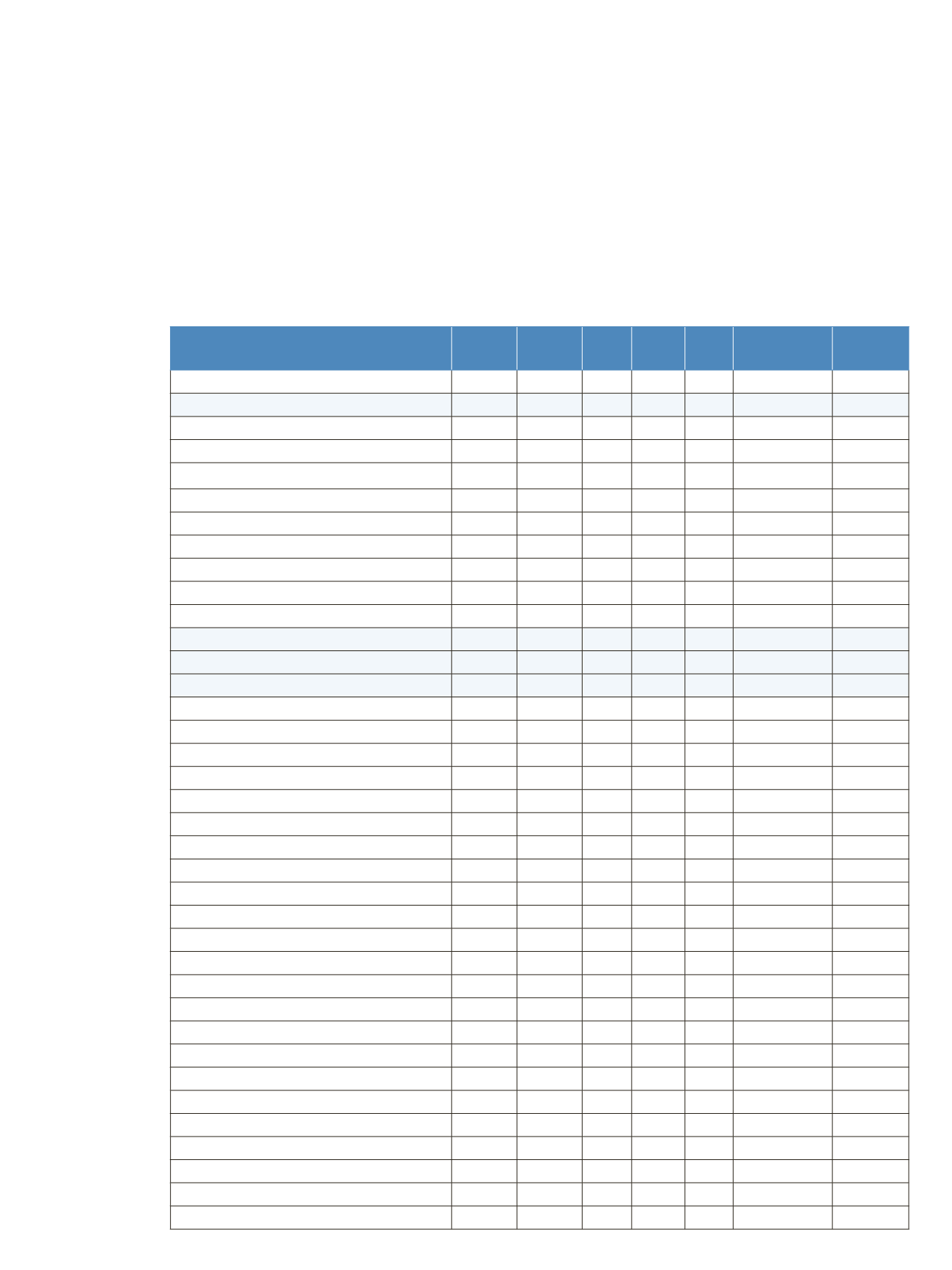
The calculation of the masses for the light chain,
unglycosylated heavy chain, and intact fully assembled
antibody is presented in Table 4, showing the step-by-step
calculation starting with the 213 respectively 451 amino
acids of the light and heavy chain. Both protein sequences
contain an N-terminal glutamine, which is anticipated to
be modified to a pyro-glutamic acid, resulting in a
deduction of mass of 17.0265 Da. Moreover, the
C-terminal lysine present in the heavy chain is likely to be
cleaved off, reducing the molecular weight by another
128.09497 Da. For assembling the intact antibody, a
total of 16 disulfide linkages is considered by abstracting
32 protons. The glycan structures on each of the two
heavy chains will add between 1217.1 and 2352.1 Da in
mass. It has to be considered that the two chains can carry
different glycans, resulting in a mixed composition, e.g.
G01/G2F. Chemical composition and masses of individual
carbohydrates are listed in Table 5. The monoisotopic and
average atomic masses of the elements used to calculate
molecular weights in Tables 4 and 5 are listed in Table 6.
Table 4. Chemical composition and step-by-step calculation of monoisotopic and average mass for the light and heavy chain, including
their modifications as well as the intact antibody rituximab with various glycoforms. Detected masses shown in Figures 4, 6, and 7 are
presented in the blue cells.


