
Quantitative Measurement of Plasma Free
Metanephrines by Ion-Pairing Solid Phase
Extraction and LC-MS/MS with Porous
Graphitic Carbon Column
Xiang He, Marta Kozak; Thermo Fisher Scientific, San Jose, CA, USA
Application
Note: 539
Key Words
• TSQ Vantage
• Hypercarb HPLC
column
• Clinical Research
• LC-MS/MS
Introduction
Plasma free metanephrine (MN) and normetanephrine
(NMN), collectively known as Pmets, are important mole-
cules for clinical research. Liquid chromatography-tandem
mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) has become widely used
to measure Pmets because of its high analytical sensitivity
and specificity.
Because Pmets are very polar, special solid phase
extraction (SPE) and chromatographic methods have been
developed for their analysis. Ion-paring (IP)-SPE, which
has been used to purify a wide range of polar compounds,
is well suited for the purification of Pmets.
Goal
To develop an LC-MS/MS method for measuring Pmets
using IP-SPE and porous graphitic carbon (PGC) column
chromatography.
Methods
Sample Preparation
Thermo Scientific HyperSep C-18 cartridges (1 mL) were
preconditioned with acetonitrile and 0.1% perfluorohep-
tanoic acid (PFHA) before samples were loaded. After
sample loading, cartridges were washed with 0.1% PFHA
and eluted with 60% acetonitrile. The eluate was dried
and reconstituted for LC-MS/MS analysis.
LC-MS/MS Conditions
LC-MS/MS analysis was performed on a Thermo Scientific
TSQ Vantage triple stage quadrupole mass spectrometer
coupled with a Thermo Scientific Accela UHPLC system.
A Thermo Scientific Hypercarb column (50 × 2.1 mm,
5 μm particle size) was used. This PGC-based column is
highly durable and ideal for retaining and resolving very
polar and hydrophilic molecules. The column temperature
was maintained at 70 °C. Mobile phases were 1% formic
acid in water with ammonium formate, and 0.1% formic
acid in acetonitrile. The LC gradient was 7 minutes long.
1
The mass spectrometer was equipped with a heated
electrospray ionization probe (HESI-II) and operated in
the positive electrospray ionization mode. MN-d3 and
NMN-d3 were used as the internal standards for MN
and NMN.
Validation
The validation procedure included tests for 1) interfer-
ence; 2) SPE recovery; 3) ion suppression; 4) lower limit of
quantitation (LLOQ), dynamic range, accuracy; 5) preci-
sion; and 6) carryover.
Results and Discussion
1. Interference
Epinephrine (EPI) and NMN share the same selected
reaction monitoring (SRM) transitions and could not be
differentiated by MS/MS analysis alone. With Hypercarb™
column chromatography, the EPI-d3 peak was baseline
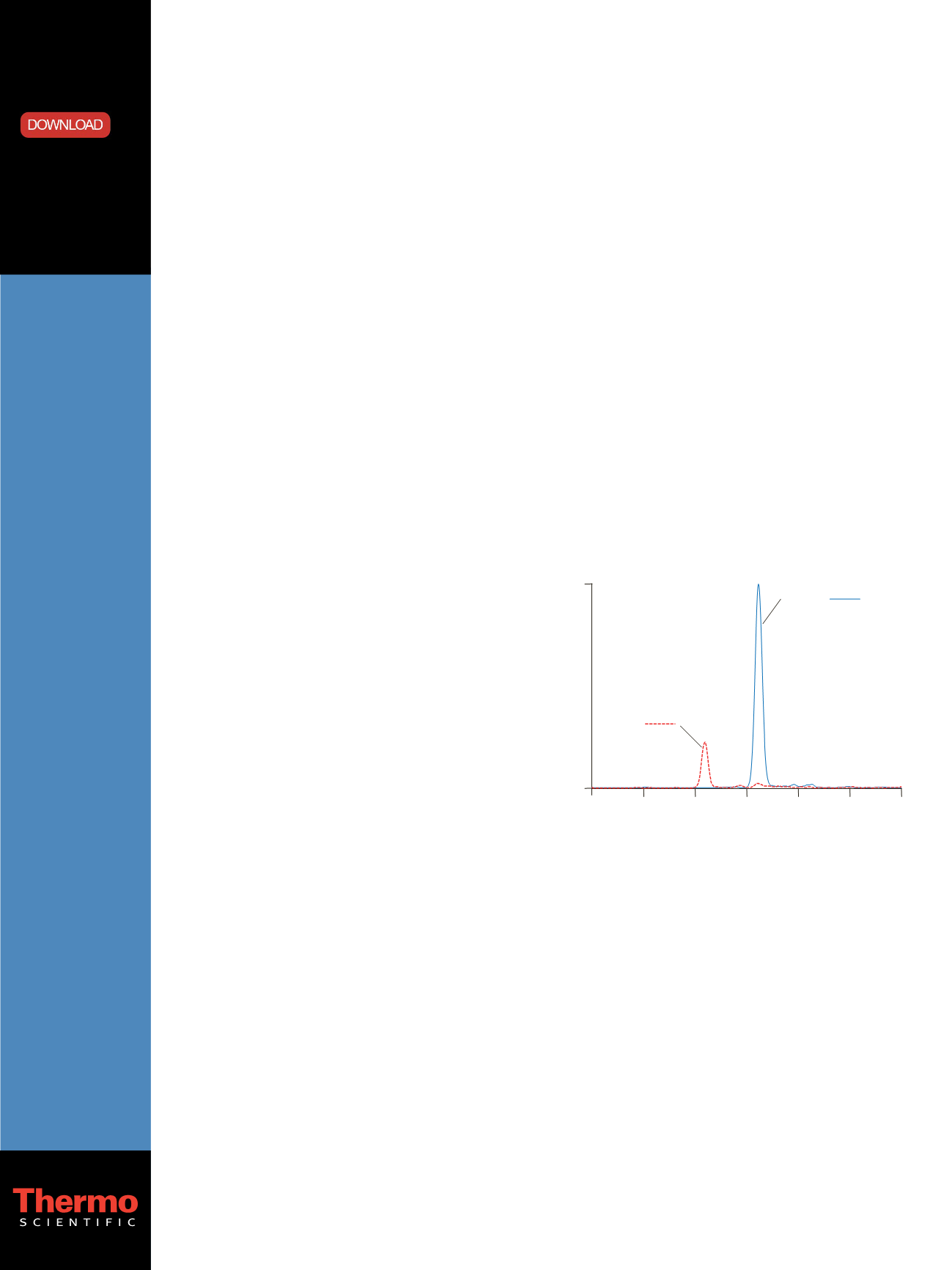
resolved from the NMN-d3 peak (Figure 1).
Figure 1. SRM chromatograms of EPI-d3 and NMN-d3 in a processed CSS
sample
Retention Time (min)
Intensity
2.2
2.4
2.7
3.0
3.3
3.6
4.0
0
16000
EPI-d3:
m/z
166 107
NMN-d3:
m/z
166 134



















