
4
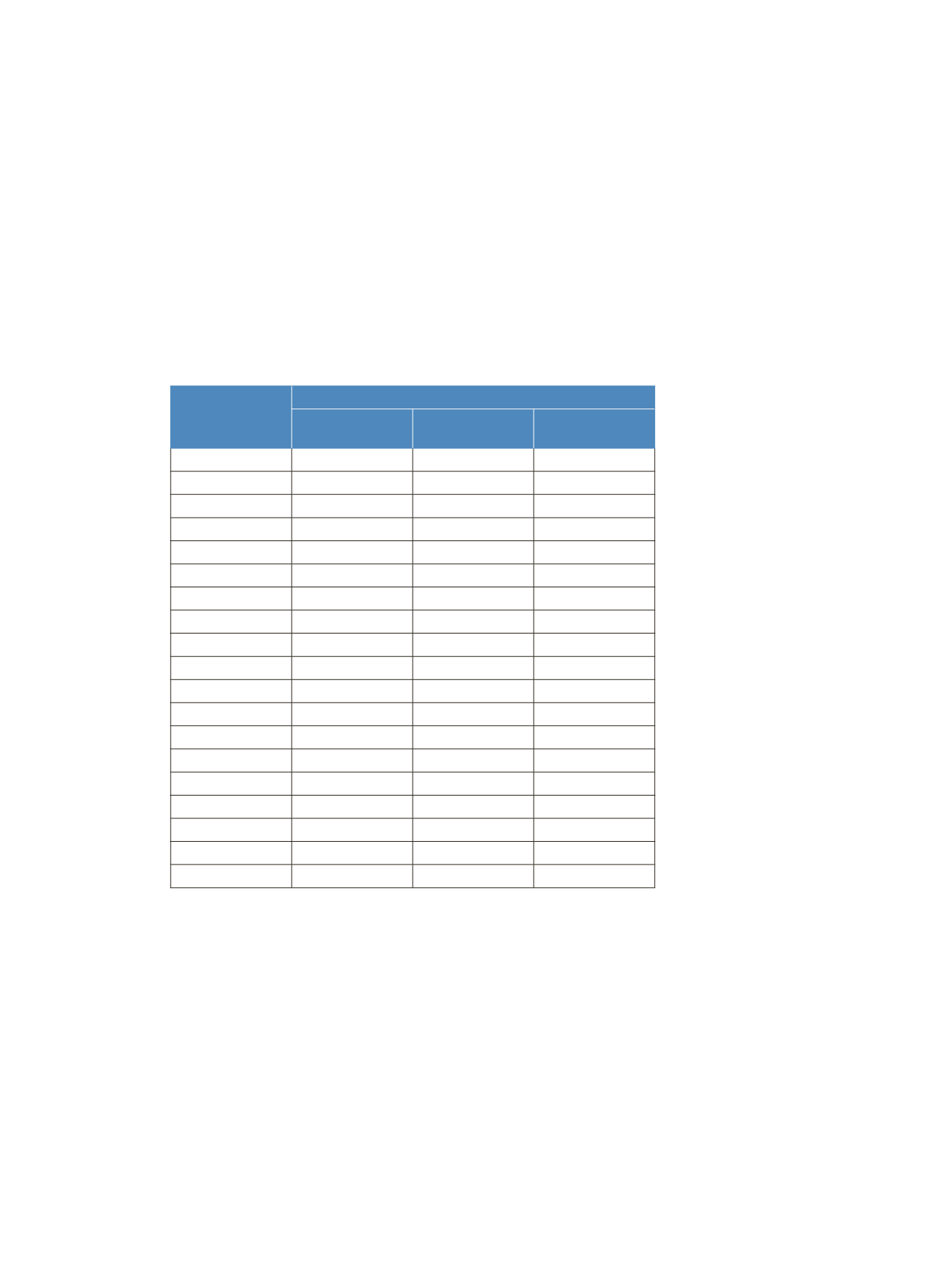
Table 4. Absolute mean signal recovery of 19 drugs at 40 ng/mL in
9 human plasma samples diluted 40-fold, 80-fold, and 200-fold,
as compared to a similarly spiked solvent blank
Analyte
(40 ng/mL)
Absolute mean signal recovery (%)
n=9
200x dilution
n=9
80x dilution
n=9
40x dilution
Amitriptyline
107.9
53.9
79.4
Bromazepam
125.7
49.7
56.6
Clobazam
78.6
43.4
54.4
Clomipramine
103.6
57.5
84.1
Clonazepam
65.9
36.0
32.3
Clozapine
81.5
60.4
56.7
Diazepam
78.4
45.6
57.9
Dothiepin
124.6
53.4
83.9
Doxepin
110.8
57.4
84.0
Flunitrazepam
77.8
44.1
51.9
Imipramine
107.2
50.6
82.8
Lamotrigine
71.5
45.1
52.8
Levetiracetam
86.7
48.2
58.3
Nitrazepam
77.8
38.4
41.7
Nortriptyline
83.7
44.5
62.2
Oxazepam
74.5
41.9
52.7
Perhexilline
94.9
152.8
190.0
Temazepam
74.7
44.6
55.1
Trimipramine
98.4
49.1
76.4
Results and Discussion
Signal Recovery
Plasma and serum are complex matrices. The matrix
content in them can significantly affect the detection of
drugs by ESI MS. Therefore, three different dilution
factors after protein precipitation (40-fold, 80-fold, and
200-fold) were compared. The LC-MS/MS signals of the
analytes in the plasma samples were compared to LC-MS/
MS signals from solvent blanks with the same spikes. The
200-fold sample dilution produced the best signal recovery
and minimum ion suppression (Table 4 and Figures 1 and
2). For all of the subsequent analyses, all samples were
prepared with a 200-fold final dilution factor.



















