24
Mobile Phase Buffer Type and Concentration
The effect of different types of ammonium salts on the retention of acid and basic model compounds was investigated
on various HILIC chemistries [27]. Ammonium formate provided longer retention times for acidic compounds on an
amino phase, due to the weaker eluting strength of the formate ion in the ion exchange interaction (as opposed to the
acetate ion which has a greater neutralizing effect of the electrostatic attractions between the surface of the positively
charged stationary phase and the negatively charged acid). Ammonium formate and ammonium acetate did not provide
differences in retention of basic analytes on the amino column. No significant differences were observed between acetate
and formate salt for neutral and zwitterionic phases.
As already pointed out, buffer salts in HILIC mobile phases are very important in reducing electrostatic interactions
between charged analytes and the stationary phase.
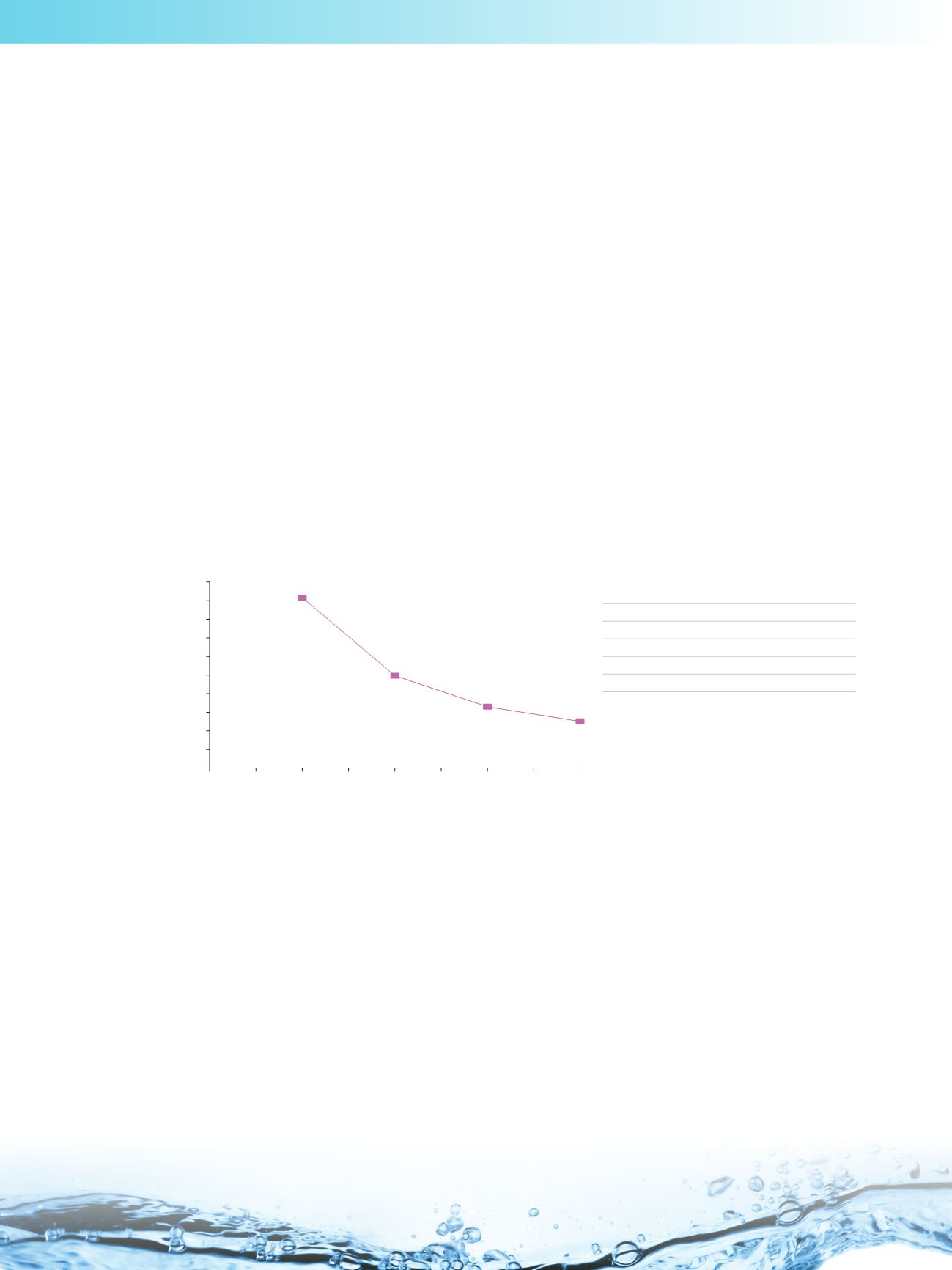
When electrostatic interactions are prevalent, an increase in the salt concentration leads to a decrease in retention of
charged solutes on the stationary phases of opposite charge. This phenomenon can be seen below, where the retention
for salicylic acid (negatively charged) on Hypersil GOLD HILIC (positively charged) decreases as the buffer concentration
increases.
k salicylic acid
Ammonium Acetate concentration (mM)
1
0
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
2.5
0
5
7.5
10
12.5
15
17.5
20
The effect of ammonium acetate concentration on the retention of salicylic acid
on Hypersil GOLD HILIC (anion exchanger)
Column:
Hypersil GOLD HILIC
, 5 µm
100 × 4.6 mm
Mobile Phase:
90/10 acetonitrile/ammonium acetate
Flow Rate:
1.0 mL/min
Inj.Volume:
5 µL
Temp.:
30 ˚C
Detection:
228 nm


