22
Apart from these, most buffers used in reversed phase should be avoided in HILIC, due to their poor solubility in highly
organic mobile phases*. Generally, negatively or positively charged stationary phases require higher concentrations of
buffers than neutral or zwitterionic phases.
Electrostatic interactions are secondary forces which can have important contributions to the retention in HILIC, since
some polar compounds can be charged at the mobile phase pH conditions typically used [8]. The presence of buffers in
the mobile phase can reduce electrostatic interactions (both attractive and repulsive) between charged analytes and the
stationary phase.
When using a gradient, we recommend adding the buffer in both mobile phases, to allow constant buffer strength to
be maintained throughout the run. For example, mobile phase A is made up of 100% aqueous buffer and mobile phase
B should contain 95% acetonitrile and 5% aqueous buffer; both mobile phases could be prepared by adding 5% of
concentrated aqueous buffer to either water or acetonitrile. We also suggest that the concentrated aqueous buffer should
be a maximum of 10 mM but not above, to avoid this solution crashing out when added to acetonitrile. The use of a
lower concentration buffer will also reduce any suppression effects that can be observed with electrospray sources either
in CAD or in MS.
* Please note that these are general recommendations. There are specific cases−e.g. USP methods for sugars−which suggest the use of phosphate
buffers in 75% acetonitrile.
Mobile Phase Buffer pH
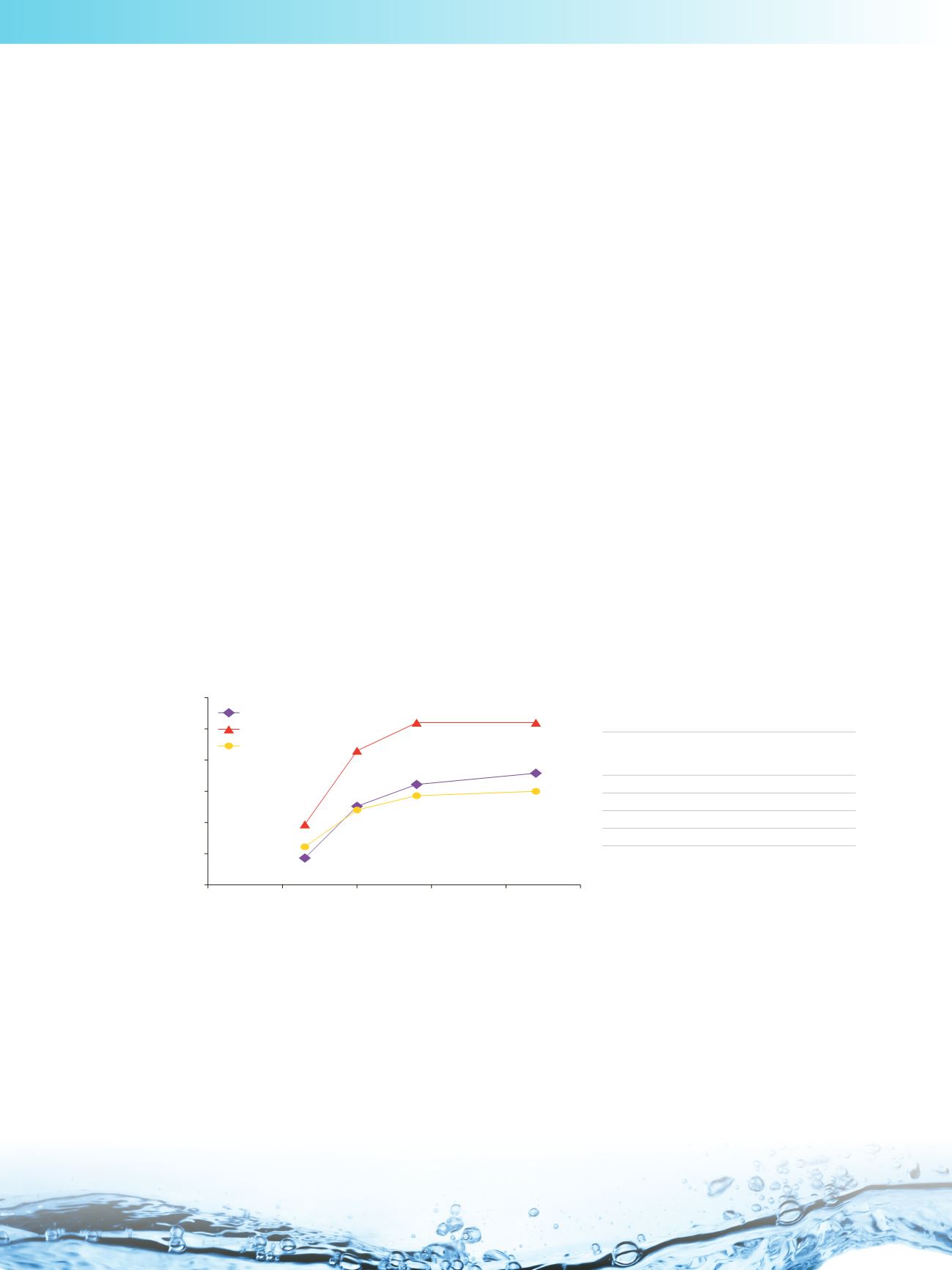
In general, charged compounds are more hydrophilic, and therefore are more retained in HILIC. The plot below shows the
retention factor of acetylsalicylic acid increasing with the buffer pH, on bare silica and zwitterionic phases:
Acetylsalicylic acid has a pK
a
of 3.5; as the buffer pH increases (pH between 4−6.5), it becomes deprotonated and hence
more retained. As the buffer pH drops below 4, the proportion of protonated acetylsalicylic acid increases, leading to less
retention*.
* Interestingly there are two effects occurring with the retention of acetylsalicyclic acid, one is the increased polarity which gives an increase in retention
and the second is the effect of the two charges of the stationary phase and also of the compound, which will have a slightly negative effect on the
retention.
k acetyl salicylic acid
Buffer pH
0
0.5
1
1.5
2
2.5
3.0
3
4
5
6
2
7
Accucore HILIC
Syncronis HILIC
Hypersil GOLD Silica
The effect of mobile phase buffer pH on the retention of acetylsalicylic acid
Columns:
Accucore HILIC
, 2.6 µm
100 × 4.6 mm
Syncronis HILIC
and
Hypersil GOLD Silica
,
5 µm 100 × 4.6 mm
Mobile Phase:
90/10 acetonitrile/100 mM ammonium
formate (the mobile phase buffer pH was
measured before the addition of acetonitrile)
Flow Rate:
1.0 mL/min
Inj.Volume:
5 µL
Temp.:
30 ˚C
Detection:
228 nm


