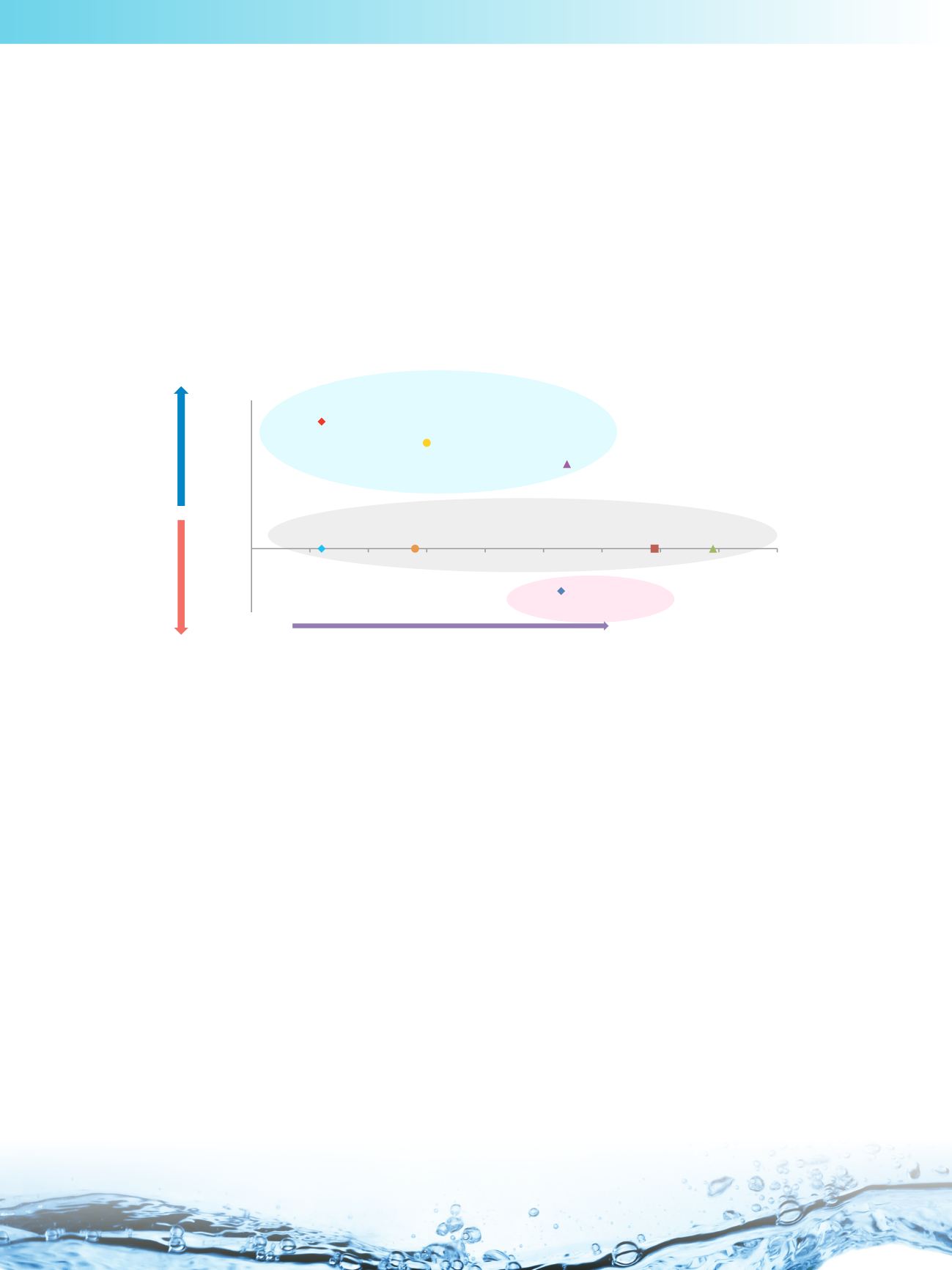
Stationary Phase Selection
Once the physiochemical properties of the analyte are known, it is then suggested to match the analyte log D values to
the degree of polarity of the HILIC phases. In general terms, the more negative the log D value for an analyte, the greater
the degree of stationary phase polarity required to retain it. The following chart, which illustrates the relative hydrophilicity
and ion-exchange properties for Thermo Scientific
™
HILIC columns, can be used as a guide in stationary phase selection
at this stage:
Stationary phase materials with a higher degree of hydrophilicity are shown on the right-hand side of the chart. So, for
example Thermo Scientific
™
Accucore
™
150-Amide-HILIC, being the most polar of these phases should be chosen for
very polar analytes (which may not get enough retention on a lesser polar phase).
Although in HILIC the predominant retention mechanism is partitioning, secondary electrostatic interactions can play an
important role in the separation.
With charged analytes it is possible to use the ion-exchange properties of the stationary phase to one’s advantage.
Materials with cation exchange properties are shown above the X-axis, whilst the phase with negative ion-exchange
properties (an anion exchanger) is shown below. So, for example, Thermo Scientific
™
Syncronis
™
silica is a material with
considerable cation exchange characteristics, and can be recommended for the analysis of basic compounds. However,
this material will not be suitable for the retention of acidic compounds*.
On the other hand, Thermo Scientific
™
Hypersil GOLD
™
HILIC, which has anion exchange properties, can be considered
for acids but will show reduced retention for basic compounds.
The materials with no ion-exchange properties, Thermo Scientific
™
Acclaim
™
HILIC-10, Thermo Scientific
™
Accucore
™
Urea-HILIC, Syncronis HILIC and Accucore 150-Amide-HILIC are suitable for both charged and neutral analytes. These
phases are therefore particularly useful where there may be a requirement to separate a mixture of acidic, basic and
neutral species. Column selection is discussed in more detail in the following section.
* Note: this might not be the case for the separation of a mixture of acids.
Relative polarity and ion-exchange characteristics for various HILIC phases
(based on study illustrated in next section)
Hypersil GOLD HILIC
Syncronis
HILIC
Accucore 150
-Amide-HILIC
Accucore HILIC
Hypersil GOLD silica
Accucore
Urea-HILIC
Syncronis silica
1.5
1.4
1.6
1.7
1.8
1.9
2.0
2.1
2.2
2.3
Acclaim
HILIC-10
Increased retention of polar compounds (degree of hydrophilicity)
Increased
retention of bases
Increased
retention of acids
Basic analytes
Neutral or charged analytes
Acidic analytes
14


