4
Comparing LC and GC Triple Quadrupole MS for the Screening of 500 Pesticides in Matrix
TSQ Quantum Access MAX
All samples were analyzed on
triple stage quadrupole mass
(HESI) source. To maximize th
SRM windows were employed
addition, Quantitation-Enhanc
triggered MS/MS data, was us
negative polarity switching wa
Figure 6 below.
LC/MS Instrument Methodology
U-HPLC Method Conditions
Chromatographic analysis was performed using the Thermo Scientific™ Accela™
1250 UHPLC system. The autosampler was an HTC-PAL™ Autosampler (CTC
Analytics, Zwingen, Switzerland). The column used was a Thermo Scientific
™
Hypersil
™
GOLD aQ column (100 x 2.1 mm, 1.9 µm particle size). Displayed in Figure
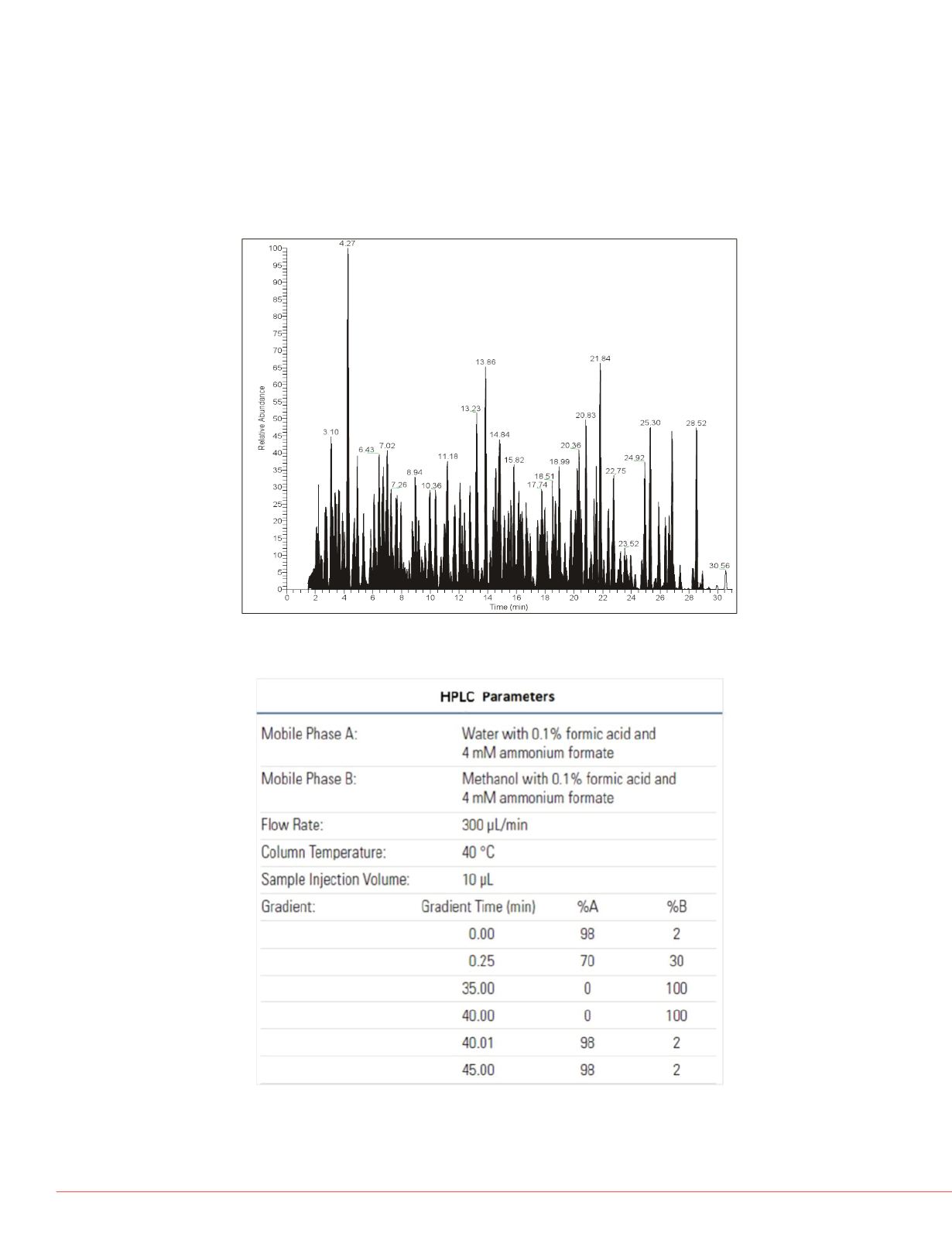
4 is the total ion chromatogram. The UHPLC conditions are listed in Figure 5.
FIGURE 5. HPLC Parameters
Results and Di
Determination of Method De
For both GC/MS and LC/MS
several concentrations close t
(EU MRL). Each concentration
determination
2
of the method
MRL for an onion matrix for ea
for the pesticide in onion, a 10
regulations.
Comparison of GC/MS to LC
The majority of compounds w
LC/MS method used (Figure 7
pesticides had MDLs less than
432 pesticides with MDLs belo
a10 µL injection was used in t
employed in the GC/MS meth
FIGURE 7. Number of comp
MRLs for GC/MS and LC/MS
rmo Scientific™ TSQ 8000
developed with the use of
development with collision
Finder™ software was used for
Selecting the appropriate
populated the SRM acquisition
essing parameters in the
ing method. One ion per
al ions were used for ion ratio
s used.
FIGURE 6. LC-Mass Spectro
FIGURE 4. LC/MS Total Ion Chromatogram
TraceGOLD™ TG-5SILMS,
r employed was a baffled,


