
3
Peptide sequences were validated using Thermo Scientific
ProteinCenter
™
software for protein functional
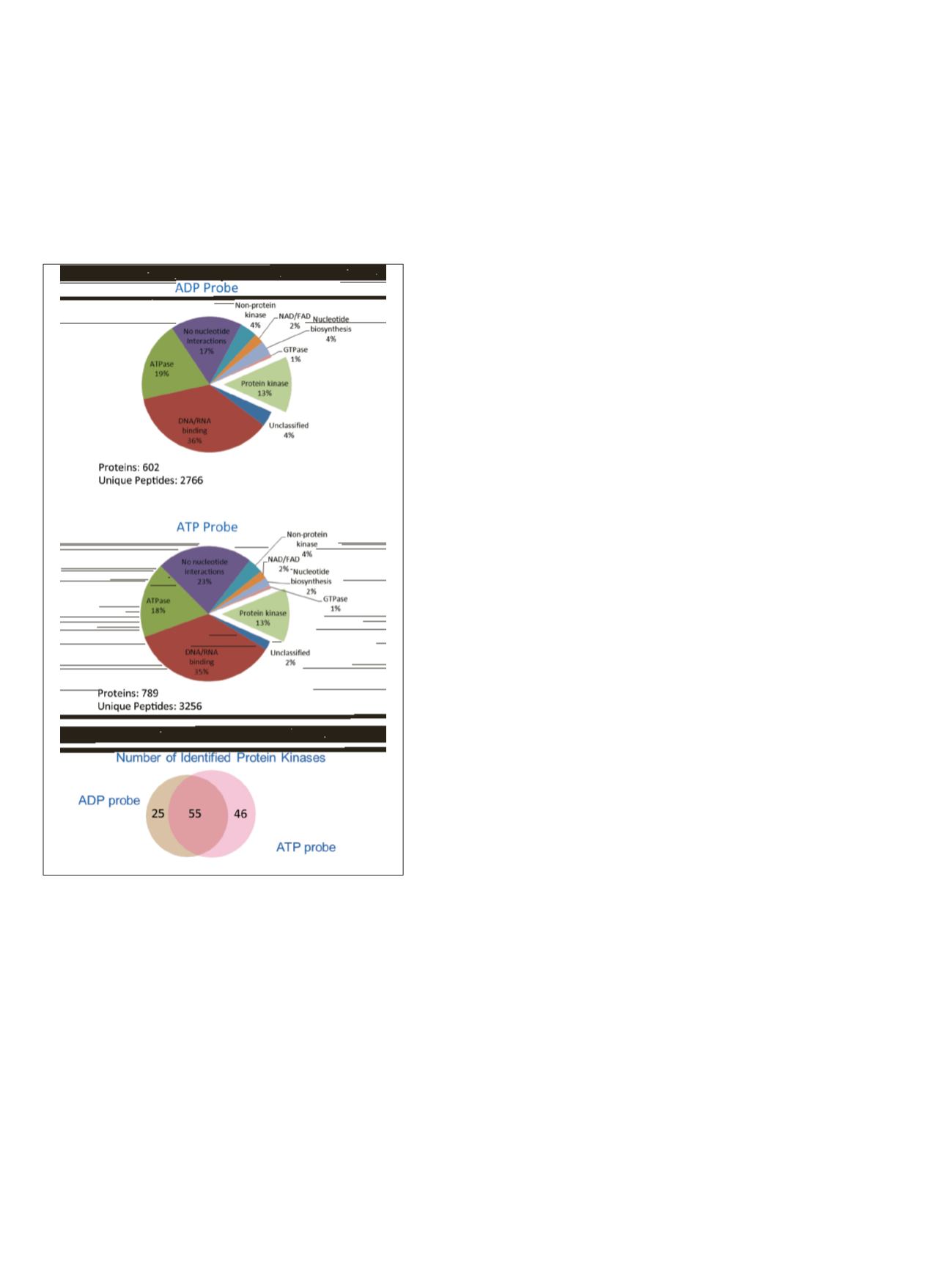
annotation. Figure 2 shows the proteins identified from
peptides labeled with either desthiobiotin-ATP or -ADP
probes. Both probes show high specificity for labeling
known ATP binding proteins (77% and 83%, respectively)
with protein kinases representing 13% of the total
proteins identified using either probe. Although both
probes enriched similar numbers of kinases with a modest
degree of overlap, there was preferential binding of each
probe for specific kinases as previously reported.
1
Figure 2. Proteins identified after desthiobiotin-ATP and -ADP
probe labeling and enrichment categorized by protein function
using Protein Center software. The Venn diagram shows the
distribution of the resulting protein kinases identified using
each probe.
The high resolution (up to 140,000) and mass accuracy of
Orbitrap detection, as well as the ability to use the C-trap
to collect/enrich the concentration of ions, facilitated kinase
active-site peptide identification at the MS and MS/MS
levels. Figure 3A shows an HR/AM MS spectrum at the
retention time of the targeted active-site peptide
DI
K
AGNILLTEPGQVK
from Tao1/3. The complexity of
the spectrum is typical even after active-site peptide
enrichment and contains numerous highly charged
peptides. The speed of the Q Exactive instrument for
serial HR/AM MS and MS/MS acquisition, coupled with
the C-trap’s enrichment of the ion concentration in the
Orbitrap mass analyzer, enabled the unbiased selection
and sequencing of the +3 precursor despite it being the
14th most abundant peptide. Figure 3B shows the
experimentally measured isotopic distribution and the
corresponding theoretical isotopic distribution for the
DI
K
AGNILLTEPGQVK
+3 precursor charge state. Each
isotope had less than 5 ppm mass error and less than 15%
error compared to the theoretical isotope intensity
distribution.
Figure 3C shows the HCD MS/MS spectra database
search result matching 25 b- and y-type fragment ions.
The average mass error for the fragment ions was less
than 2 ppm across an order of magnitude range of
measured product ion intensities. The ability to maintain
a constant mass error across the entire mass spectrum is a
particular advantage of Orbitrap detection, as it greatly
increases peptide identification confidence. Ultimately,
126 kinase active-site peptides identified using Proteome
Discoverer software were imported into Pinpoint software
to evaluate relative abundance and generate an inclusion
list for scheduled targeted acquisition (Figure 3D).



















