
4
Analyte
Start
Time
(min)
Stop
Time
(min)
Ionization
Mode
Precursor
Ion Mass
(
m/z
)
Product
Ion Mass
(
m/z
)
Collision
Energy
(V)
Tube
Lens
(V)
PEMA
0.6
1.6
+
207.1
91.2
25
70
207.1
119.2
15
207.1
162.1
10
Primidone
0.8
1.8
+
219.0
91.2
25
90
219.0
119.2
15
219.0
162.1
10
IS13
0.8
1.8
+
224.0
167.1
20
90
IS5
0.8
1.8
+
243.0
182.1
5
100
Phenytoin
1.1
2.1
+
253.0
104.1
20
100
253.0
182.0
15
253.0
225.0
10
Stiripentol
1.3
2.3
+
217.0
145.1
16
55
217.0
159.1
13
217.0
187.1
10
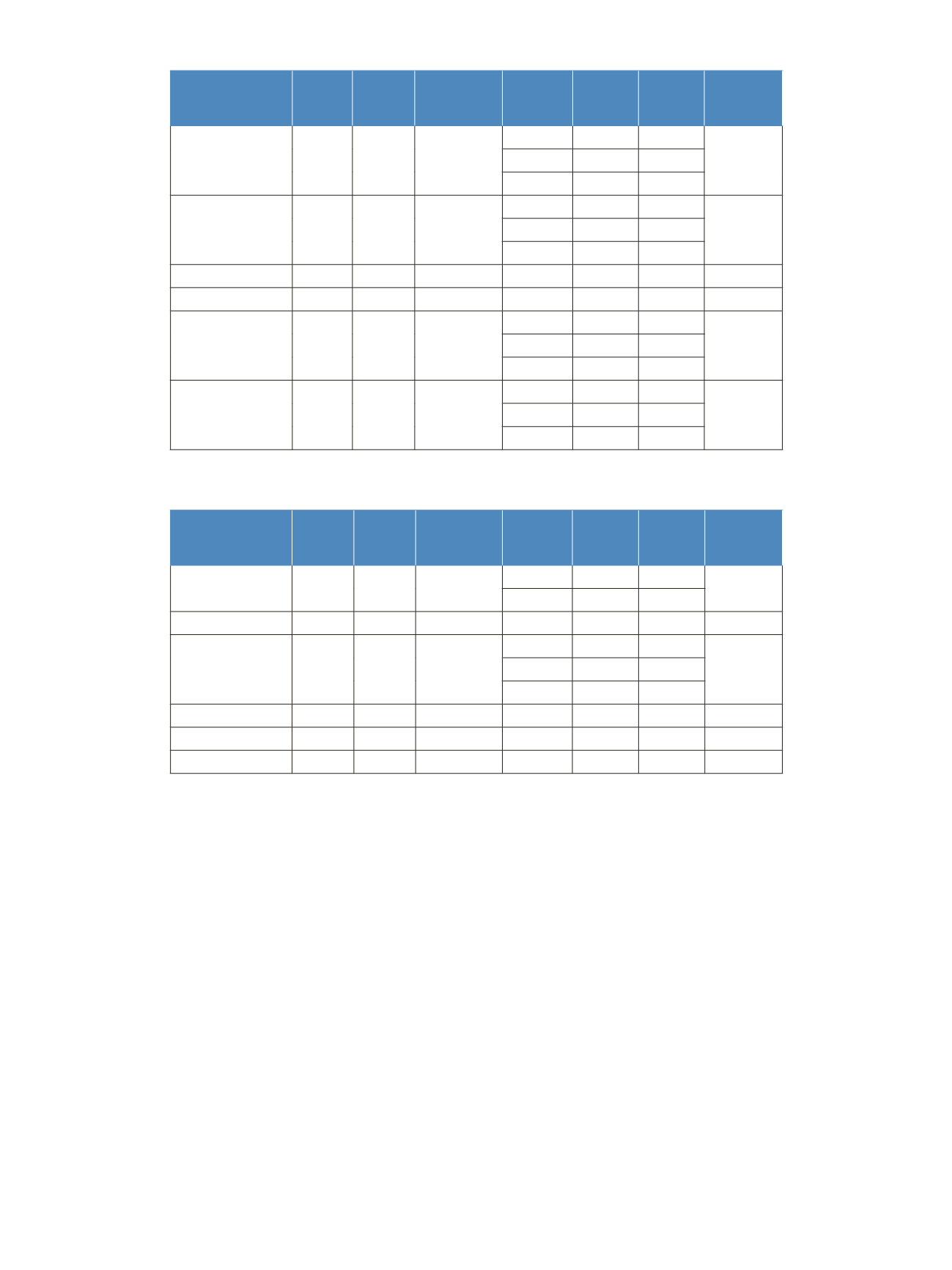
Table 4. SRM settings – Group 2
Analyte
Start
Time
(min)
Stop
Time
(min)
Ionization
Mode
Precursor
Ion Mass
(
m/z
)
Product
Ion Mass
(
m/z
)
Collision
Energy
(V)
Tube
Lens
(V)
Zonisamide
0.7
1.7
-
211.1
119.1
18
70
211.1
147.1
12
IS18
0.7
1.7
-
216.0
123.2
15
70
Phenobarbital
0.9
1.9
-
231.0
85.3
15
70
231.0
144.2
15
231.0
188.0
10
IS16
0.9
1.9
-
236.0
193.1
10
70
Valproic Acid
1.2
2.2
-
143.1
143.1
10
70
IS17
1.2
2.2
-
147.1
147.1
10
70
Table 5. SRM settings – Group 3
Data Acquisition and Processing
Data were quantitated using a linear regression, and 1/x
weighting was used to build the calibration curves.
Maximum percentage bias between nominal and
calculated concentration of 15% and 20% was set as
acceptance criterion for calibrators and controls,
respectively.
Results and Discussion
Linear calibration curves were obtained for all the
analytes in the evaluated concentration ranges, and
correlation factors (R
2
) were always above 0.99. The
percentage bias between nominal and experimental
concentration for all calibrators and controls was always
within the set acceptance criteria (15% for calibrators and
20% for controls). A summary of calibration range,
intercept, slope, and correlation factor (R
2
) for each
analyte is reported in Table 6.



















