
Thermo Fisher Scientific,
San Jose, CA USA is
ISO 13485 Certified.
AN64047-EN 1014S
Africa
+43 1 333 50 34 0
Australia
+61 3 9757 4300
Austria
+43 810 282 206
Belgium
+32 53 73 42 41
Canada
+1 800 530 8447
China
800 810 5118
(free call domestic)
400 650 5118
Denmark
+45 70 23 62 60
Europe-Other
+43 1 333 50 34 0
Finland
+358 9 3291 0200
France
+33 1 60 92 48 00
Germany
+49 6103 408 1014
India
+91 22 6742 9494
Italy
+39 02 950 591
Japan
+81 45 453 9100
Korea
+82 2 3420 8600
Latin America
+1 561 688 8700
Middle East
+43 1 333 50 34 0
Netherlands
+31 76 579 55 55
New Zealand
+64 9 980 6700
Norway
+46 8 556 468 00
Russia/CIS
+43 1 333 50 34 0
Singapore
+65 6289 1190
Spain
+34 914 845 965
Sweden
+46 8 556 468 00
Switzerland
+41 61 716 77 00
UK
+44 1442 233555
USA
+1 800 532 4752
www.thermoscientific.com©2014 Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc. All rights reserved. ISO is a trademark of the International Standards Organization.
All other trademarks are the property of Thermo Fisher Scientific and its subsidiaries. This information is presented as an
example of the capabilities of Thermo Fisher Scientific products. It is not intended to encourage use of these products in any
manners that might infringe the intellectual property rights of others. Specifications, terms and pricing are subject to change.
Not all products are available in all countries. Please consult your local sales representative for details.
Application Note 612
References
1. Kuypers, D.R.; Le Meur, Y.; Cantarovich, M.,
et al.
Consensus report on therapeutic drug monitoring
of mycophenolic acid in solid organ transplantation.
Clinical Journal of the American Society of
Nephrology
: CJASN 2010;5:341-58.
2. COMMISSION DECISION of 12 August 2002
implementing Council Directive 96/23/EC concerning
the performance of analytical methods and the
interpretation of results. Official Journal of the
European Communities. L 221/8. 17.8.2002.
http://faolex.fao.org/docs/pdf/eur49615.pdf3. U.S. Food and Drug Administration, Guidance for
Industry, Bioanalytical Method Validation 2001.
(http://www.fda.gov/downloads/Drugs/GuidanceComplianceRegulatoryInformation/
Guidances/UCM070107.pdf).
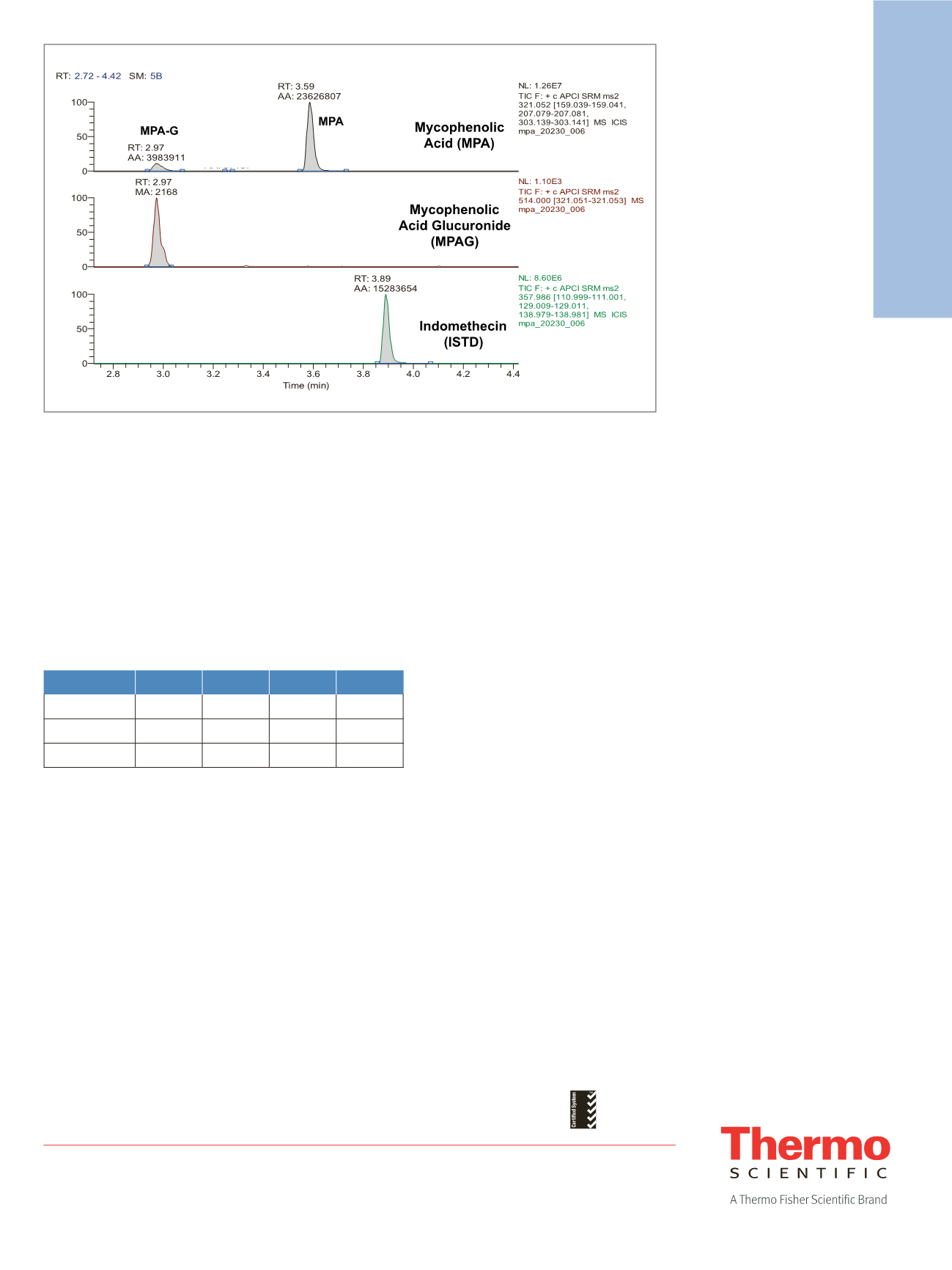
Figure 1 presents a chromatogram showing the three
SRM scans. MPA and MPAG peaks are separated by
a retention time (RT) difference of approximately
0.6 minutes on the scan for the [M+H]
+
ion of MPA.
For quantitative analysis of the metabolite, maximum
conversion of MPAG to MPA is driven by optimizing
the severity of the ionization process.
The calibration curve was linear from 0.2 mg/L to
40 mg/L. Precision data is presented in Table 4 showing
CVs of 5.8–6.4% across the calibration range of the assay.
Conclusion
The research method developed using TurboFlow
technology allowed an accurate detection and
quantification of MPA. It is also fast, requires minimal
manual sample preparation, and conforms to current
guidelines.
Table 4. Interday precision study for LC-MS/MS analysis of MPA.
Four levels of quality control material, 10 replicates per level,
repeated over 5 consecutive days.
QC1
QC2
QC3
QC4
MEAN mg/L
1.7
6.9
11.3
33.5
STD DEV
0.1
0.4
0.7
1.9
CV%
6.4
6.3
6.2
5.8
Figure 1. Extracted ion chromatograms for MPA (top), MPAG (middle), and internal standard (bottom)
For research use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
ISO 13485



















