8
LC-MS Analysis of Native
N
-Glycans Released
from Proteins
The GlycanPac AXH-1 column is also suitable for
analysis of native glycans. Analyzing unlabeled glycans
not only eliminates the extra reaction step and cleanup
methods during labeling, but also retains the original
glycan profile without adding further ambiguity imposed
by the labeling reaction.
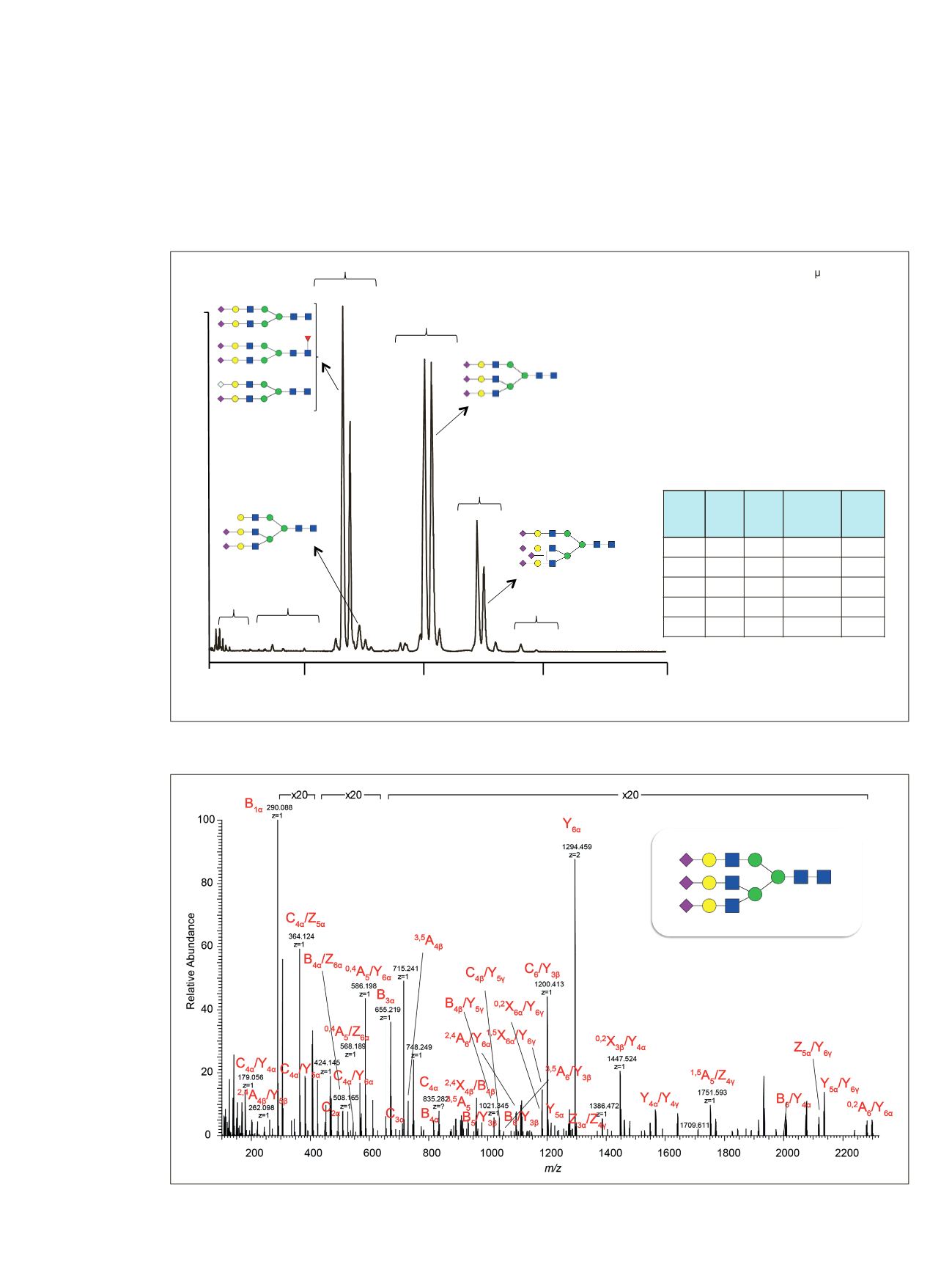
Figure 3 shows the LC/MS analysis of native
N
-glycans
from bovine fetuin using the GlycanPac AXH-1 column.
Detailed information is in Table 3. A representative
MS/MS spectrum for a trisialylated triantennary glycan
is shown in Figure 4.
Figure 3. LC/MS analysis of native
N
-glycan from bovine fetuin
2
10
20
30
40
0
100
Relative Abundance
Neutral Monosialylated
Disialylated
Trisialylated
Tetrasialylated
Pentasialylated
1 2
3 4 5 a-c
6
7a-c
8 a-c
9
10
11 12 13
14
15 16
17
18
19
20
21 22 23
Minutes
Column:
GlycanPac AXH-1, 1.9 m
Dimension:
2.1 x 150 mm
Mobile phase:
A: Acetonitrile/water (80:20, v/v)
B: Ammonium formate (80 mM, pH 4.4)
Flow:
0.4 mL/min
Temp:
30
o
C
Injection:
500 pmol
Detection:
MS detector, Q Exactive
Sample:
Native N-glycan from bovine fetuin
MS mode:
Negative
Orbitrap mass range: m/z = 380–2000
Time
(min)
% A
% B
Flow
Rate
(mL/min)
Curve
-10
97.5
2.5
0.4
5
0
97.5
2.5
0.4
5
30
87.5
12.5
0.4
5
35
75.0
25.0
0.4
5
40
62.5
37.5
0.4
5
7a
7b
7c
9
16
20
Figure 4. MS/MS spectra for a native trisialylated triantennary
N
-glycan released from bovine fetuin


