
2
Detection of Cellular Response to an in vitro Challenge with Bacterial Gram-Negative Lipopolysaccharides (LPS) in Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells (PBMCs)
Overview
Purpose:
To find differentially expressed marker proteins for sepsis in an
in vitro
model environment.
Methods:
Blood from healthy volunteers is treated with toxic ligands secreted by
gram-negative bacteria. PBMCs are isolated, reduced, alkylated, digested with trypsin.
The resulting peptides are analyzed using liquid chromatography-tandem mass
spectrometry (LC-MS/MS). Differential peptides are identified by Thermo Scientific™
Proteome Discoverer™ software and compared using Thermo Scientific™ Pinpoint™
software.
Results:
Full scan quantification of several hundred relevant kinase and pathway
specific proteins generated from over 4000 identified proteins.
Introduction
Gram-negative bacteria, and a major component, lipo-polysaccharides (LPS), are
associated with sepsis. In this study, we look at global protein profiling of mononuclear
cells from LPS-challenged whole blood.
Mononuclear cells are easy to collect and have little of the protein dynamic range
difficulties associated with plasma. In addition, they are responsive to many immune
state conditions, making them ideal targets for biomarker discovery experiments.
Using an
in vitro
stimulation using a whole blood system directly in tubes used for the
isolation allows for a highly facile method for looking for changes in either secreted
proteins in the plasma fraction or for quick-onset protein changes in the PBMC cell
fraction.
As most gram-negative sepsis infections are from
E. coli
, we chose the corresponding
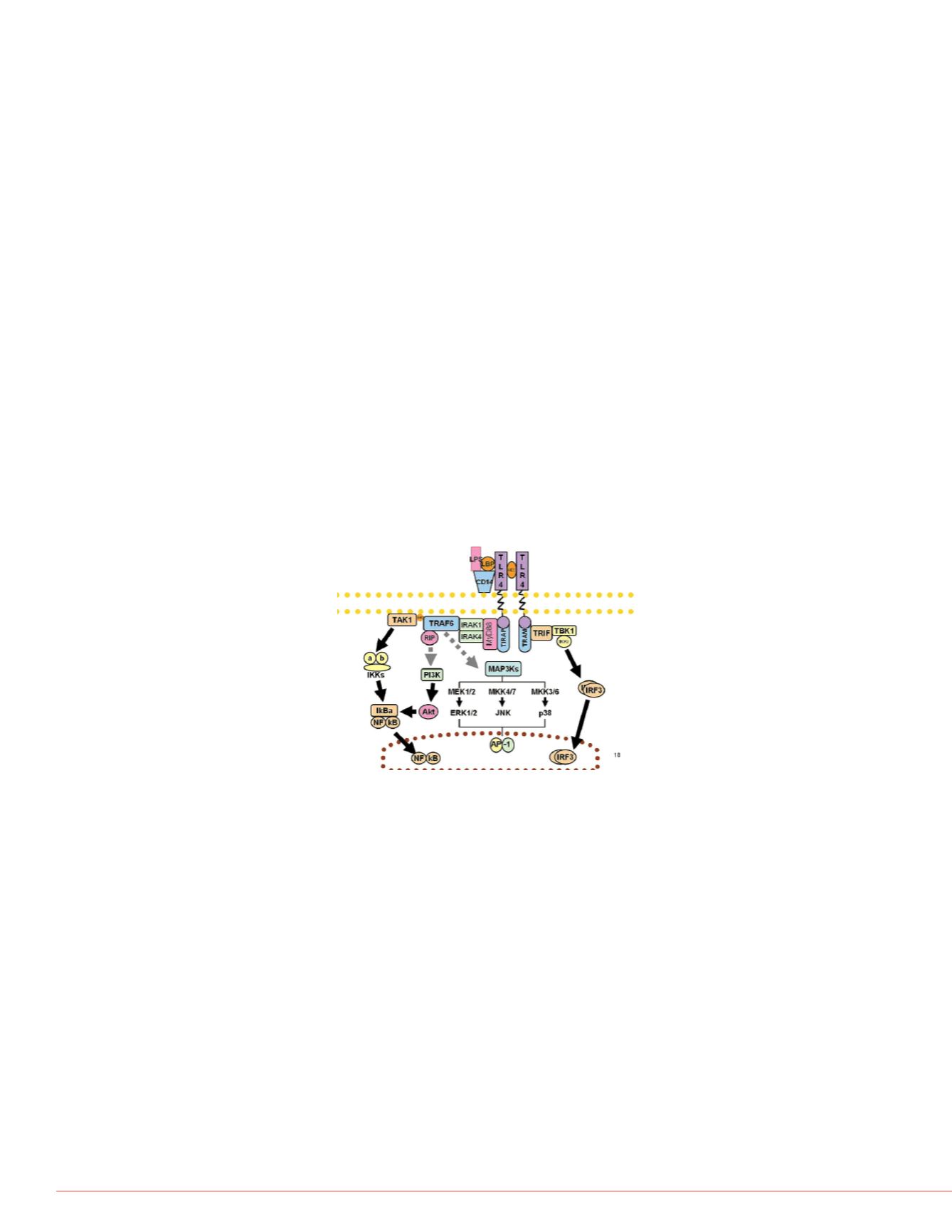
LPS. LPS from rod shaped bacteria stimulates the specific Toll like receptor 4(TLR4) in
the MyD88 pathway. Toll like receptors are part of the innate immune response
pathways.
Cascades in this pathway involve many signaling events that are either proteolytic
cleavages, phosphorylations or other modifications. The large number of human
proteins and their associated post-translational modifications (PTM) represent a
challenge for MS-based biomarker discovery. To this effect, the simplest sample
preparation techniques will provide the most reproducible results.
Methods
Sample Preparation
Blood samples from a healthy single donor were collected into BD Vacutainer™ CPT
Cell Separation Tubes (Becton Dickinson) in accordance with IRB approval. Buffers
and stimulant solutions were injected directly into the blood collection tubes using a
1 mL syringe with a 27 ga needle. Control tubes had 200 µL of phosphate buffered
saline added and were prepared in parallel to the stimulated tubes. LPS-EB Toll Like
Receptor 4 Ligand (InvivoGen, San Diego, CA) was added to a concentration of
100 ng/mL (Low stim) and 10 µg/mL (High stim) of whole blood.
After incubation at 37 ºC for 3
manufacturerʼs instructions for
(~2 mg) were denatured in 35
10 mM Dithiothreitol, reduced/
and digested overnight with 20
Liquid Chromatography
Peptide retention time standar
plates onto a Thermo Scientifi
Thermo Scientific™ Dionex™
x 12 cm) connected in a “vent
100 µm x 50 cm packed tip re
Flex™ Ion Source on a hybrid
Flow and gradient from 4-50%
0.2% formic acid, water(v/v). B
0.2% formic acid (v/v), all solv
Portions of each of the TLR4 d
were fractionated into 12 fracti
8 µm particle 300A pore, buffe
hydroxide, Buffer B: 29 mM a
using a flow rate of 1 mL/min i
Mass Spectrometry
For mass spectrometric analy
Full MS scans acquired at a re
dependent scans analyzed in t
Uncharacterized charge states
phase triggering with monoisot
minimum peak threshold of 3.
was set to 100 ms. Dynamic e
Data Analysis
Full-scan comparisons were m
processed by Proteome Disco
different peptide identification
3) only searches for high-confi
complex search strategy (Figu
nodes, where small groups of
in each node. This allows for
of each database, albeit at an
information was processed usi
shown). Pinpoint software allo
obtained from data from both
chromatography in all samples
FIGURE 2. High pH reverse
phase fractionation for libra
peptide fractionation
FIGURE 3. Search
workflow for protein
phosphorylation.
FIGURE 1. MyD88 Pathway



















