
5
Methods Characterization / Validation
Before using 3’-OH-stanozolol glucuronide and the
metabolites for doping control purposes, the fit-for-
purpose of initial testing and confirmation approaches
were determined using typical methods. The resulting
method characteristics and validated parameters are
summarized in Table 1.
Excretion Study Urine Samples
In order to estimate the utility of the newly identified
metabolites to prolong and/or improve the detection of
stanozolol abuse, the traceability of stanozolol-
O
-
glucuronide, stanozolol-
N
-glucuronide, 17-epistanozolol-
N
-glucuronide, 16
β
-OH-stanozolol-
O
-glucuronide,
4
β
-OH-stanozolol-
O
-glucuronide, and 3’-OH-stanozolol-
O
-glucuronide by the above mentioned screening method
was assessed in administration study urine samples. In
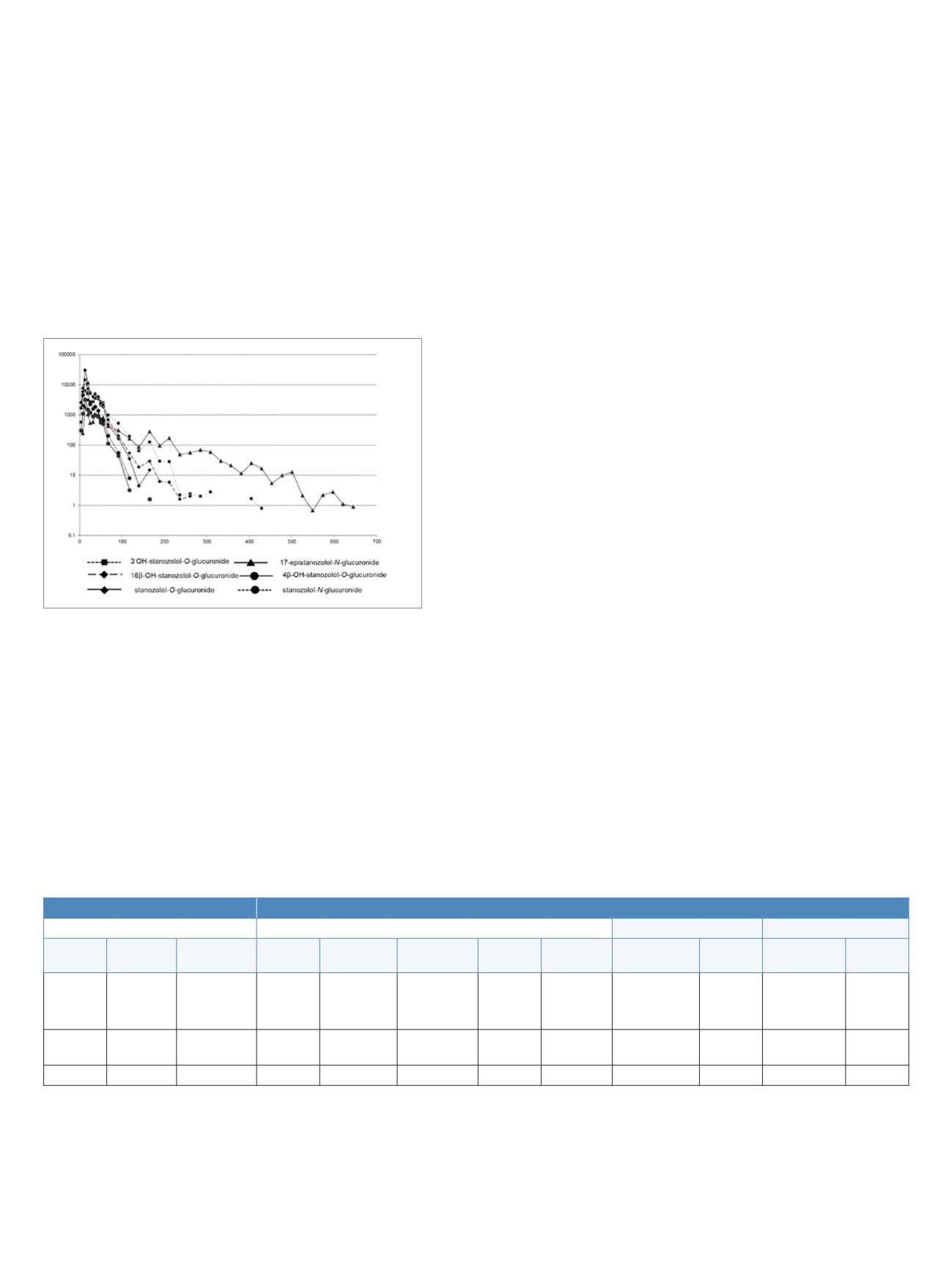
Figure 5, the intensities (log scale) of analyte signals were
plotted against the time points of urine sampling,
demonstrating considerably longer visibility of
17-epistanozolol-
N
-glucuronide, which was detected
up to 672 h (28 days) post-administration.
Figure 5. Pharmacokinetics of six metabolites monitored in the
administration study urine samples collected after application
of 5 mg of stanozolol. The N-glucuronide of 17-epistanozolol was
detected up to 28 days.
Table 1. Method characteristics and validated parameters
Dilute-and-Inject Assay
Confirmation Assay
Intraday Precision (n=30)
Interday Precision
LOD
(pg/mL)
Specificity
Ion
Suppression
LOD
(pg/mL)
Specificity
Ion
Suppression
Recovery
(%)
Calibration
Curve (n=30+30+30)
CV (%)
Concentration
(pg/mL)
CV (%)
20
No
Interference
(10+10)
3–45%
5
No
Interference
(10+10)
15–84% 106
25–150
pg/mL
25
15
25
16
Linear
(r
2
= 0.994)
100
9
100
10
250
7
250
7



















