
Detection of Stanozolol Glucuronides in
Human Sports Drug Testing by Means
of High-Resolution, Accurate-Mass
Mass Spectrometry
Wilhelm Schänzer
1
, Sven Guddat
1
, Andreas Thomas
1
, Georg Opfermann
1
, Hans Geyer
1
, and Mario Thevis
1,2
1
Institute of Biochemistry - Center for Preventive Doping Research, German Sport University Cologne, Cologne,
Germany;
2
European Monitoring Center for Emerging Doping Agents, Cologne/Bonn, Germany
Application Note 613
Key Words
Sports doping, antidoping testing, Q Exactive Focus, long-term metabolite,
anabolic agents, 16-oxo-stanozolol, stanozolol glucuronide, epistanozolol
Goal
To demonstrate the utility of direct dilute-and-shoot analysis of glucuronic
acid conjugates of stanozolol by means of liquid chromatography and high-
resolution, accurate-mass mass spectrometry in sports antidoping testing.
To characterize and validate, by means of commercially available
3’-OH-stanozolol glucuronide, “dilute and inject” and confirmation methods,
which will allow for the unambiguous identification of stanozolol misuse in
routine doping-control samples.
Introduction
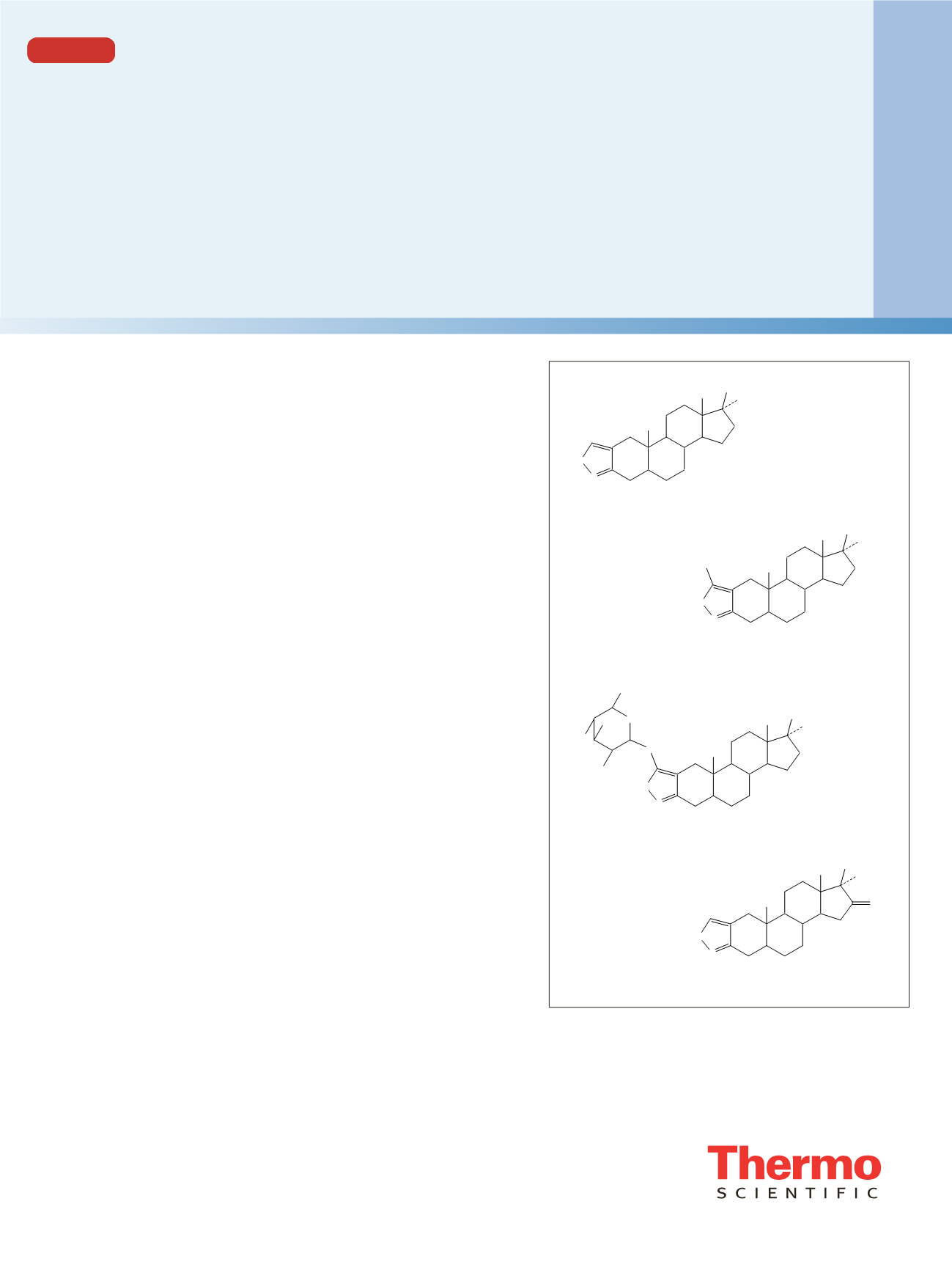
The analysis of the anabolic steroid stanozolol (Figure 1a)
has proved to be challenging for gas chromatography
mass spectrometry (GC-MS) methods due to stanozolol’s
peculiar physicochemical properties. The uncovering of
stanozolol abuse by means of its major urinary metabolite
3’-OH-stanozolol (Figure 1b) as accomplished by
Schänzer and Donike
1
initiated investigations into the
metabolic fate of this anabolic agent. The molecular
features of stanozolol and its metabolites demand
sophisticated derivatization and separation steps for
GC/MS-based methodologies. Methods based on liquid
chromatography with electrospray-ionization tandem
mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS), on the other hand,
provide benefits such as lower limits of detection (LODs)
and detection windows with expanded metabolite
identification. 3’-OH-stanozolol glucuronide (Figure 1c) is
the latest metabolite analyzed at 25–50 pg/mL in human
urine. In the present study, the use of high-resolution,
accurate-mass mass spectrometry for the detection of
3’-OH-stanozolol glucuronide is outlined. Complementary
information on N-conjugated glucuronide metabolites of
stanozolol and 17-epistanozolol and the use of these in
routine doping controls is provided.
Figure 1. Chemical formulae of stanozolol (a. C
21
H
32
ON
2
, mol
wt = 328.2515), 3’-OH-stanozolol (b. C
21
H
32
O
2
N
2
, mol wt =
344.2464), 3’-OH-stanozolol-O-glucuronide (c. C
27
H
40
O
8
N
2
, mol
wt = 520.2785), and 16-oxo-stanozolol (d. C
21
H
30
O
2
N
2
, mol wt =
342.2307)
a.
Stanozolol
b.
3’-OH-stanozolol
c.
3’-OH-stanozolol-
O
-glucuronide
d.
16-oxo-stanozolol
1
7
6
5
4
3
3'
2
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
O
HO
OH
HO
COOH
HN
N
CH
3
CH
3
OH
CH
3
HN
N
CH
3
CH
3
HO
HN
N
CH
3
CH
3
OH
CH
3
O
HN
N
CH
3
CH
3
a.
Stanozolol
b.
3’-OH-stanozolol
c.
3’-OH-stanozolol-
O
-glucuronide
d.
16-oxo-stanozolol
1
7
6
5
4
3
3'
2
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
O
HO
OH
HO
COOH
HN
N
CH
3
CH
3
OH
CH
3
HN
N
CH
3
CH
3
OH
CH
3
HO
HN
N
CH
3
CH
3
OH
CH
3
O
HN
N
CH
3
CH
3
OH
CH
3
O
a.
Stanozolol
b.
3’-OH-
c.
3’-OH-stanozolol-
O
-glucuronide
d.
16-ox
1
7
6
5
4
3
3'
2
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
O
HO
OH
HO
COOH
HN
N
CH
3
CH
3
OH
CH
3
HN
N
CH
3
HO
HN
N
CH
3
CH
3
OH
CH
3
O
HN
N
CH
3
a.
Stanozolol
b.
3’-OH-stanozolol
c.
3’-OH-stanozolol-
O
-glucuronide
d.
16-oxo-stanozolol
1
7
6
5
4
3
3'
2
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
O
HO
OH
HO
COOH
HN
N
CH
3
CH
3
OH
CH
3
HN
N
CH
3
CH
3
OH
CH
3
HO
HN
N
CH
3
CH
3
CH
3
O
HN
N
CH
3
CH
3
OH
CH
3
O



















