
5
Thermo Scientific Poster Note
•
PN-MSACL-2014-Spectral-Libraries-Frewen_E_03/14S
down the list
and
-house script
0 peptides in all
often A came
et.
ng
lotted at their
data. The
to act as
each of three
s is the same
e same
with a higher
of landmark
ry run, but
Conclusion
Endogenous peptides can successfully act as retention time landmarks and
accurately estimate RT in new gradients.
Spectrum libraries capture valuable retention time information.
Our algorithm finds endogenous peptides with consistent elution behavior to
act as standards.
We can accurately predict the retention time of any library peptide by
estimating it relative to the standard peptides. Therefore, comparisons can
more easily be made across datasets with accurate mass and retention time
measurements (AMT). This capability also enables method transfer to
scheduled LC-MRM.
Library-based estimated retention times are closer to the observed times
than predictions made based on hydrophobicity.
References
1. Krokhin OV, Spicer V. (2009) Peptide retention standards and
hydrophobicity indexes in reversed-phase high-performance liquid
chromatography of peptides.
Anal Chem
81(22):9522-30.
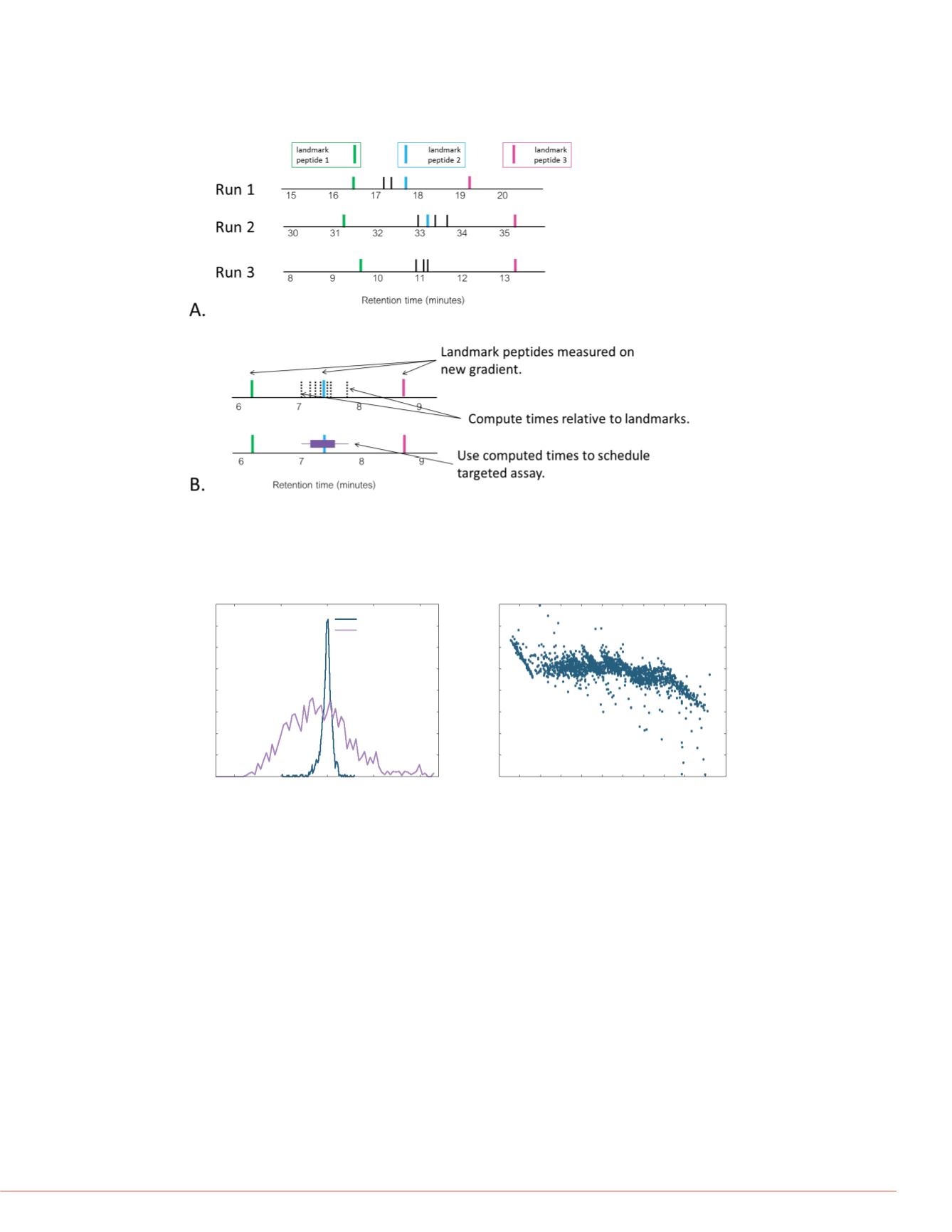
FIGURE 3. A. Observed retention times of target peptides are stored as the
distance between the two nearest landmark peptides. B. Retention time
predictions are made by projecting the relative times on to the known
times of the landmarks on a new gradient.
FIGURE 4. Comparison of estimated and observed retention times of 1750
peptides. A. Histogram of predicted minus observed retention times for
both prediction methods. B. Library-predicted minus observed retention
time vs. the observed retention time.
de stored in
. (Figure 3a)
-100
-50
0
50
100
-20
-30
-40
-10
0
10
20
30
Time difference (minutes)
60
40
20
80
100
120
140
160
Number of peptides
10
-50
220 240
180 200
140 160
100 120
60 80
20 40
Time difference (minutes)
Retention time (minutes)
A
B
Library
Hydrophobicity



















