
2
General analytical conditions
The iCAP Qc ICP-MS was equipped with a peltier cooled
PFA spray chamber and a PFA-LC nebulizer (Elemental
Scientific, Omaha, NE, USA). The PFA-LC nebulizer has a
very low dead volume and is compatible with LC fittings
making it ideal for chromatographic analyses. The
demountable torch was equipped with a 2 mm I.D.
injector. For interference-free detection of
52
Cr
+
and
53
Cr
+
,
all measurements were carried out in a single collision cell
mode, with kinetic energy discrimination (KED), using
pure He as collision gas.
The instrument was operated using the following
parameters:
Parameter
Value
Forward power
1550 W
Nebulizer gas
0.80 L/min
Injector
2 mm I.D.
Cell gas flow / KED voltage
4.8 mL/min He / 2V
Dwell time
100 ms
Table 1: iCAP Q operating parameters.
Chromatographic separations on the ICS-5000 were
carried out using the parameters summarized in Table 2.
For the elution of the different Cr species, anion exchange
chromatography was chosen using isocratic elution with
nitric acid. Although the two species have different
charges, (Cr (III) is present predominantly as [Cr(H
2
O)
6
]
3+
and Cr (VI) as H
2
CrO
4
, HCrO
4
-
, CrO
4
2-
or Cr
2
O
7
2-
depending on the pH), the Dionex AG-7 column can elute
both due to its capacities for the separation of both
cations and anions3. In contrast to other techniques based
on reversed phase ion pairing chromatography, no prior
incubation with complexing agents such as EDTA is
required with the method described. Sample pre-treatment
is therefore no longer required, eliminating any possible
risk of contamination as well as maximizing sample
throughput. Under the applied conditions, complete
separation of Cr (III) and Cr (VI) is accomplished in less
than 150 s.
Column
Dionex AG-7 (2 mm i. D., 50 mm length)
Elution
Isocratic
Mobile phase
0.4 mol/L HNO
3
Flow rate
400 µL/min
Injection volume 20 µL
Duration
150 s
Table 2: ICS-5000 operating parameters
Coupling between instruments was achieved by direct
connection of the column outlet to the nebulizer.
Bi-directional communication was established by using a
trigger cable that attached to the I/O panel next to the
iCAP Q’s sample introduction system. All quantification
(evaluation of peak areas and concentrations etc) were
achieved using the tQuant features of the Thermo
Scientific Qtegra control software.
Results and Discussion
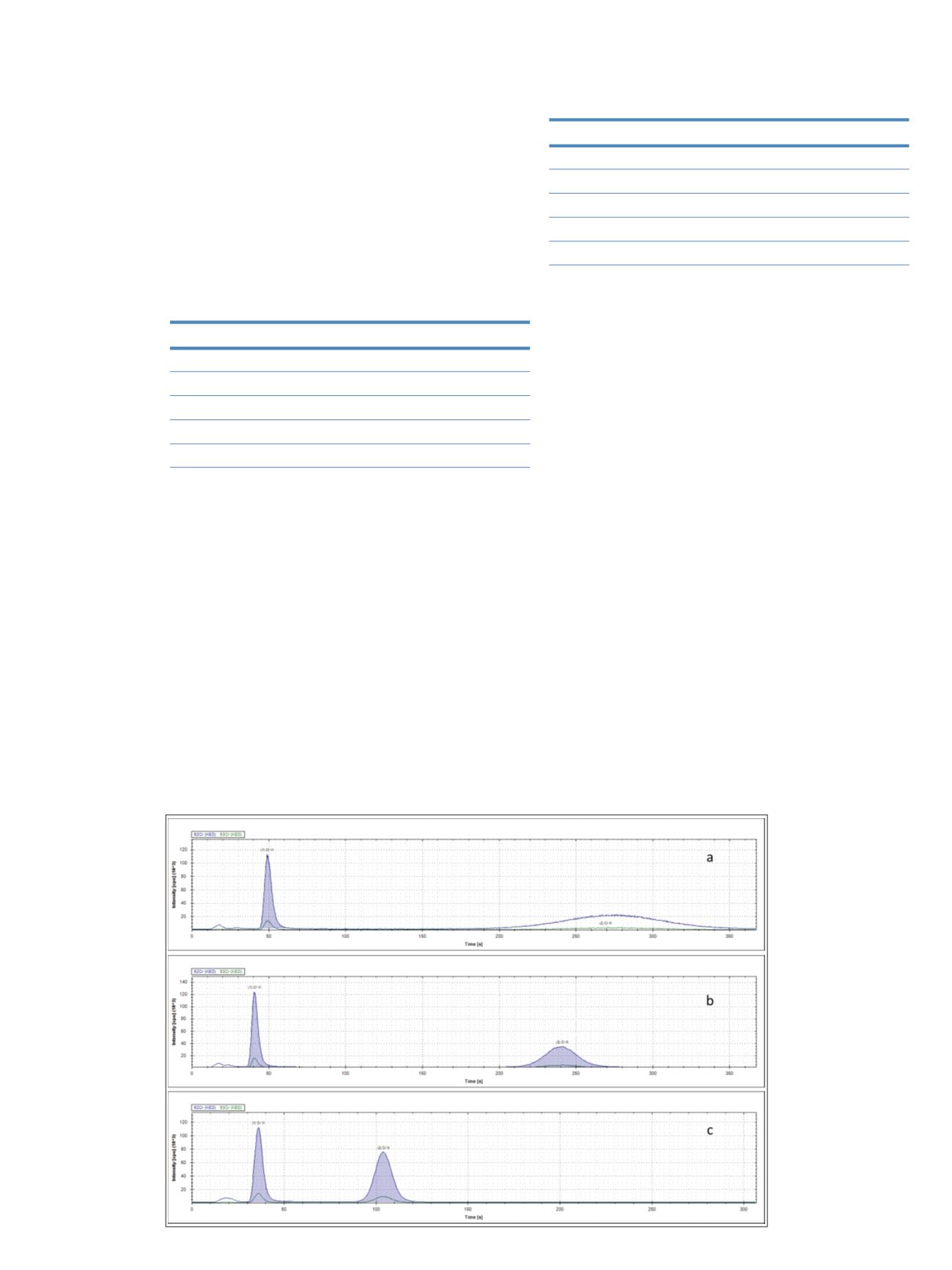
For initial method development, a mixture containing
5 ng/g of each Cr species was separated using different
mobile phases. The resulting chromatograms are shown in
Figure 1 as screenshots from the Qtegra
™
software
package. While the Cr (VI) was easily eluted from the
column with all the mobile phases tested, Cr (III) was
strongly retained and only eluted as a distinguishable peak
at nitric acid concentrations higher than 0.3 mol/L. At
even higher concentrations, however, the redox potential
of Cr (VI) is increased and could potentially lead to its
reduction and therefore possible loss. For this reason, a
compromise nitric acid concentration limited to 0.4 mol/L
was used for the elution of both Cr species in this study.
At this concentration, cycle times of under 150 s were
achieved for a complete separation of Cr (III) and Cr (VI).
Fig. 1: Cr (III) and Cr
(VI) chromatograms
obtained using 0.2
(a), 0.3 (b) and 0.4 (c)
mol/L nitric acid as
mobile phase. Please
note that the x-axis in
(c) has been shortened
to 300 s.



















