
In addition to these
offices, Thermo Fisher
Scientific maintains
a network of represen-
tative organizations
throughout the world.
Africa-Other
+27 11 570 1840
Australia
+61 2 8844 9500
Austria
+43 1 333 50 34 0
Belgium
+32 2 482 30 30
Canada
+1 800 530 8447
China
+86 10 8419 3588
Denmark
+45 70 23 62 60
Europe-Other
+43 1 333 50 34 0
Finland/Norway/
Sweden
+46 8 556 468 00
France
+33 1 60 92 48 00
Germany
+49 6103 408 1014
India
+91 22 6742 9434
Italy
+39 02 950 591
Japan
+81 45 453 9100
Latin America
+1 608 276 5659
Middle East
+43 1 333 50 34 0
Netherlands
+31 76 579 55 55
South Africa
+27 11 570 1840
Spain
+34 914 845 965
Switzerland
+41 61 716 77 00
UK
+44 1442 233555
USA
+1 800 532 4752
www.thermo.comAN63041_E 06/09S
Part of Thermo Fisher Scientific
Thermo Fisher Scientific,
San Jose, CA USA is ISO Certified.
Legal Notices
©2009 Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc. All rights reserved. Milli-Q is a registered trademark of Millipore Corporation. All other trademarks are the property of
Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc. and its subsidiaries. This information is presented as an example of the capabilities of Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc. products. It is
not intended to encourage use of these products in any manners that might infringe the intellectual property rights of others. Specifications, terms and pricing
are subject to change. Not all products are available in all countries. Please consult your local sales representative for details.
View additional Thermo Scientific LC/MS application notes at:
www.thermo.com/appnotesConclusion
We developed and successfully
applied an APCI-LC-MS/MS method
for quantifying a wide range of
compounds from a diverse group of
pharmaceuticals, pesticides, and
personal care products at
concentration in the low ng/L range
in surface waters with good precision
and accuracy. Results confirmed the
presence of pharmaceuticals, personal
care products, and endocrine
disruptors in all water resources
around the region of Montreal. The
concentrations of compounds
fluctuated with sampling locations
due to the variation of these sources,
wastewater contamination and
combined sewer overflow discharges.
References
1. T. A. Ternes and A. Joss, Eds., Human
Pharmaceuticals, Hormones and Fragrances:
The Challenge of Micropollutants in Urban
Water Management,
IWA
, 2006, p 443.
2. A. Kortenkamp,
Env. Health Perspective
,
2007, pp 1-42.
3. C. Hao, L. Lissemore, B. Nguyen, S. Kleywegt,
P. Yang, K. Solomon,
Anal. Bioanal. Chem.
,
2006, 384, 505-513.
4. C. D. Metcalfe, X-S Mia, W. Hua, R. Letcher,
M. Servos,
Pharmaceuticals in the Canadian
Environment. In Pharmaceuticals in the
Environment: Sources, Fate, Effects and Risks
,
second edition; K. Kummerer, Ed.; Springer-
Verlag, 2004, 67-87.
5. F. Gagnè, C. Blaise, C. Andrè,
Ecotoxicology
and Environmental Safety
2006, 64, 329-336.
6. P. A. Segura, A. Garcia-Ac, A. Lajeunesse, D.
Ghosh, C. Gagnon and S. Sauvè,
J. Environ.
Monitor.
, 2007, 9, 307-313.
7. R. A. Trenholm, B. J. Vanderford, J. C. Holady,
D. J. Rexing and S. A. Snyder,
Chemosphere
,
2006, 65(11), 1990-1998.
8. C. Zwiener and F. H. Frimmel,
Anal. Bioanal.
Chem
, 2004, 378, 862-874.
9. T. A. Ternes,
Trends Anal. Chem
., 2001, 20(8),
419-434.
10. S. Souverain, S. Rudaz, J-L. Venthey,
J.
Chrom. A
, 2004, 1058, 61-66.
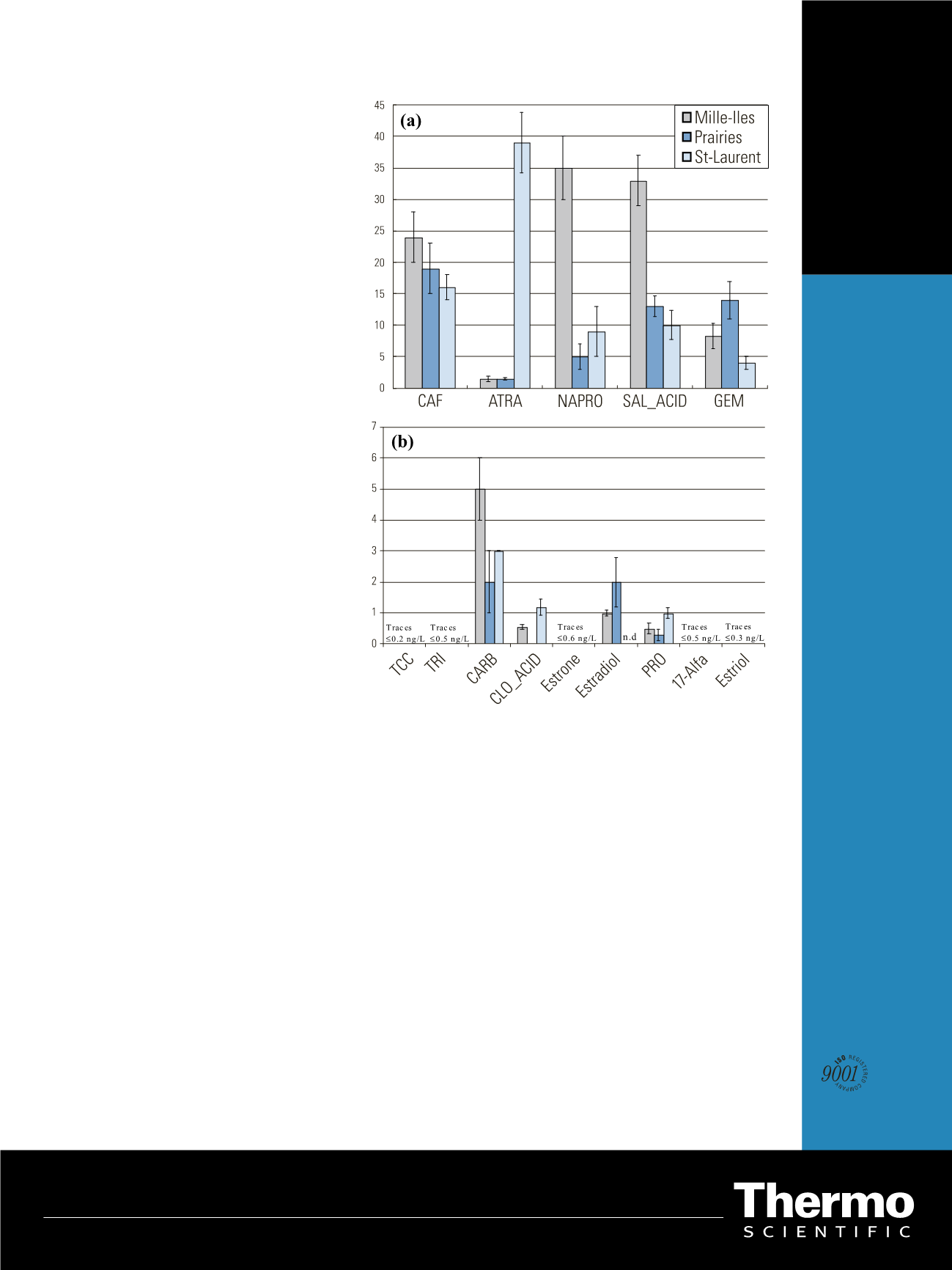
Figure 5: (a) The highest mean concentrations of selected compounds in water samples
collected from Mille-Iles River, des Prairies River and St-Laurent River (n = 6). (b) The
lowest mean concentrations of selected compounds in water samples collected from
Mille Iles River, des Prairies River and St-Laurent River (n = 6).
11. B. J. Vanderford, R. A. Pearson, D. J. Rexing
and S. A. Snyder,
Anal. Chem.
, 2003, 6265-
6274.
12. J. B. Schilling, S. P. Cepa, S. D. Menacherry,
L. T. Barda, B. M. Heard and B. L. Stockwell,
Anal. Chem.
, 1996, 68, 1905.
13. L. Y. T. Li, D. A. Campbell, P. K. Bennett and
J. D. Henion,
Anal. Chem.
, 1996, 68, 3397.
14. T. Reemtsa,
Trends Anal. Chem
., 2001, 20,
533-542.



















