
7
Thermo Scienti c Poster Note
•
PN HUPO13_POS-02-041_APrakash
_E 09/13S
(C)
Phospho (S,T,Y);
Deamidated
(N,Q);
Carboxymethyl
(C)
Oxidation (M);
Acetyl (K)
ehensive searching
We found that on
eptide identifications
ld with our
ndard searches,
edium confidence
ore than two times
to increase the
ications (FDR≤0.01)
roups by 75% with
Moreover, the
gh-confidence group
e peptides for every
veral high-confidence
ls the importance of
rch node (Table 2).
creases number of
ne, sample 2-4 =
w increases the
ith at least two
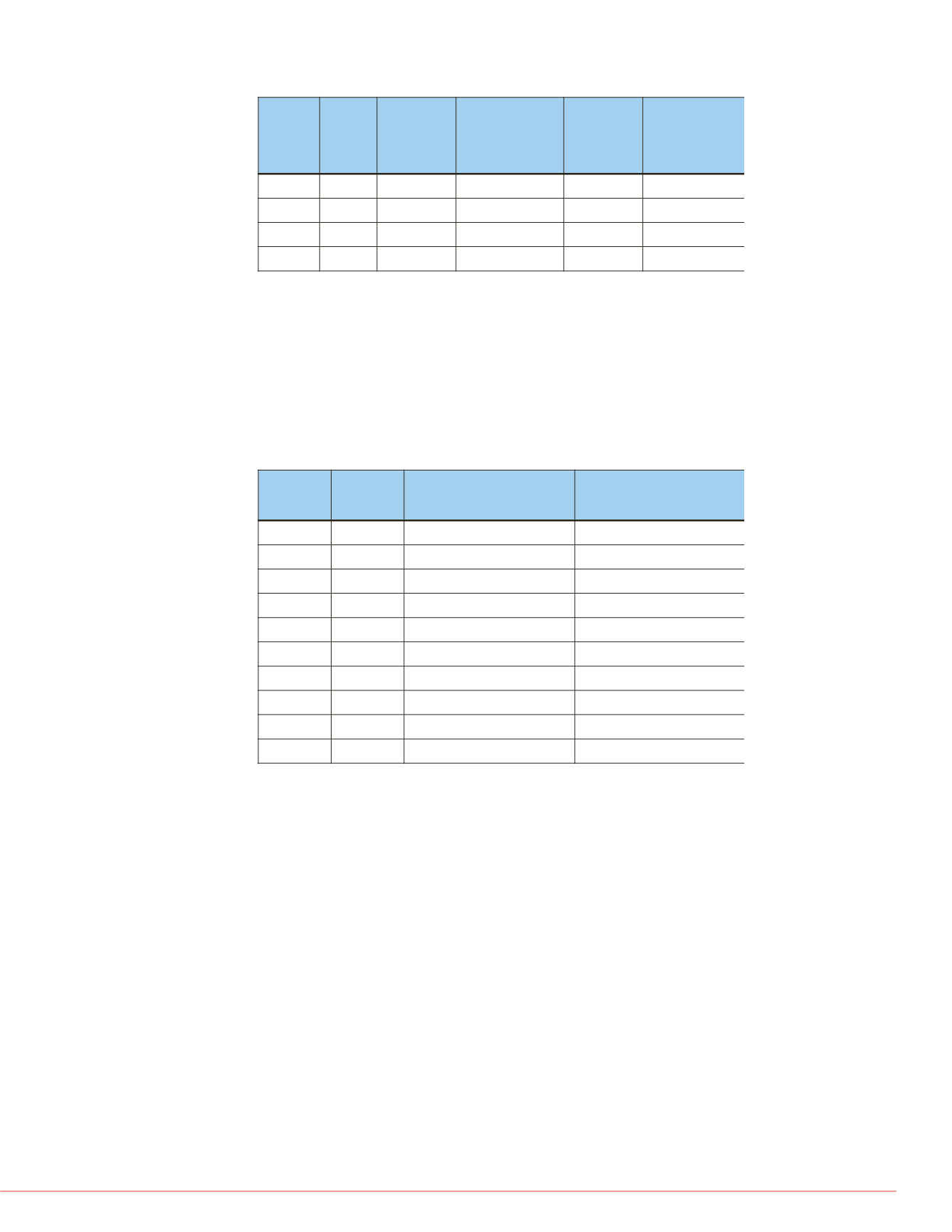
comprehensive search workflow (Table 3).
Conclusion
A comprehensive workflow strategy identified almost twice
as many high-confidence peptides compared to the
standard search strategy.
The comprehensive workflow helped increase the number
of high-confidence protein identifications and high-
confidence protein group identifications by approximately
90% and 75%, respectively, compared to the standard
search approach.
The comprehensive workflow identifies more high-
confidence peptides with multiple PTMs.
The percentage of matched spectra improves significantly
when using the comprehensive search workflow in
Proteome Discoverer software.
References
1. Khoury GA, Baliban RC, Floudas CA. Proteome-wide post-
Table 3. Comparative table for matched spectra
File
Total
Spectra
Matched
Spectra
Standard
Search
(FDR≤0.05)
Matched
Spectra
Comprehensive
Search
(FDR≤0.05)
Matched
Spectra
Standard
Search
(FDR≤0.01)
Matched Spectra
Comprehensive
Search (FDR≤0.01)
Sample1
27215
28.0%
46.7%
26.2%
41.1%
Sample2
14005
15.4%
44.2%
14.4%
39.6%
Sample3
43036
5.1%
13.6%
4.9%
12.1%
Sample4
44450
9.5%
22.3%
9.0%
20.3%
Example
Protein
Sequence Coverage
Standard Search
(FDR≤0.01)
Sequence Coverage
Comprehensive Search
(FDR≤0.01)
1
A1AT
28.47%
57.42%
2
ALBU
70.94%
78.00%
3
A2MG
35.35%
53.12%
4
AACT
35.7%
42.55%
5
APOB
14.66%
23.12%
6
CERU
22.44%
37.28%
7
HEMO
38.96%
49.13%
8
TRFE
40.11%
61.17%
9
TTHY
54.42%
62.59%
10
VTDB
31.65%
50.21%
Table 4. Comprehensive search increases protein
coverage
Moreover, the comprehensive search workflow increased
sequence coverage of proteins significantly, giving rich
information about proteins including PTMs (Table 4).



















