
6
Direct Analysis using Paper-Spray Mass Spectrometry: Method Development for the Rapid Screening of Drugs of Abuse for Forensic Toxicology
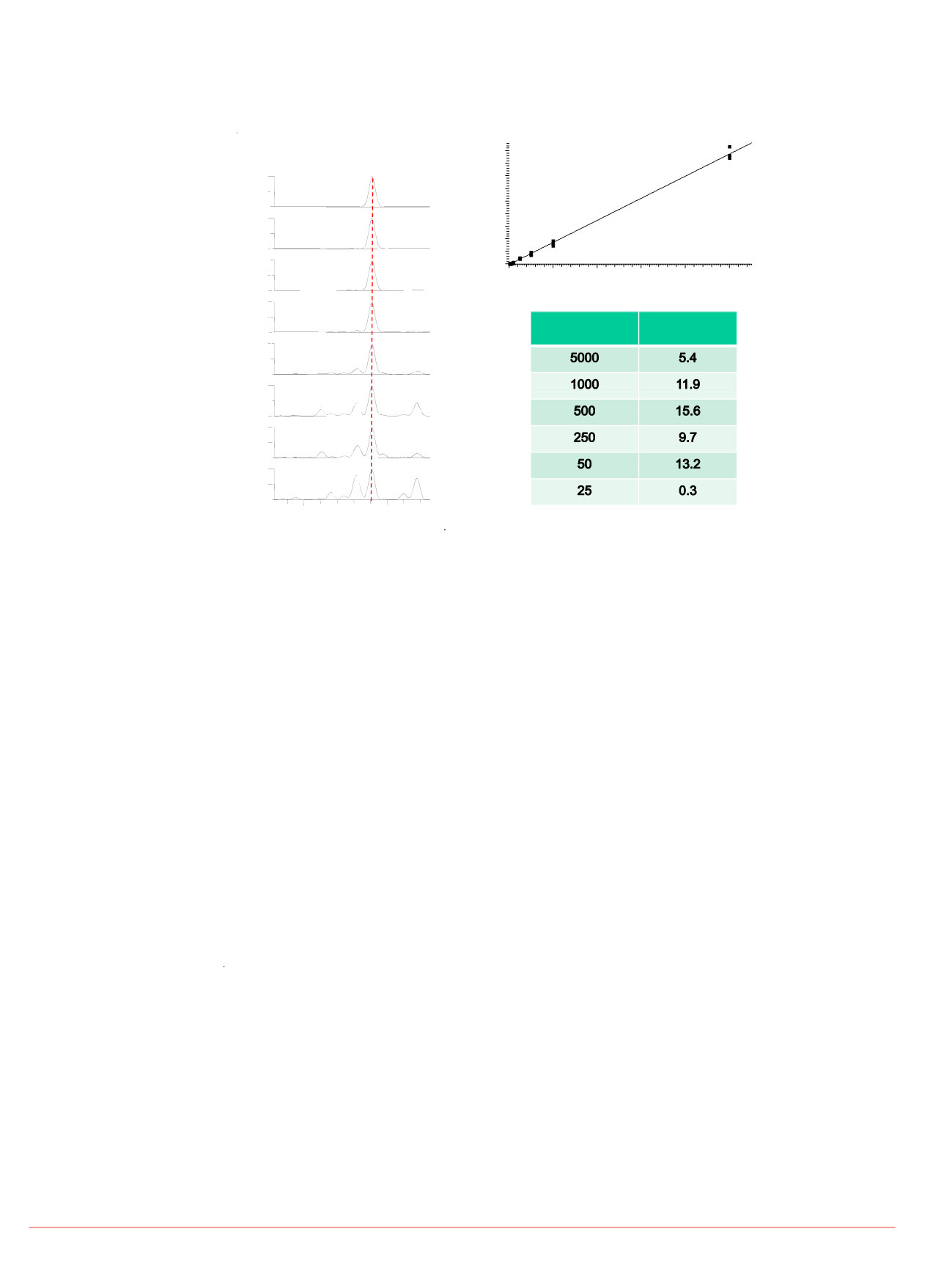
FIGURE 6b. Quantitative results for
it i t li
li d b i t
l
FIGURE 6a. Full scan MS spectra for
,000 resolving power (FWHM
. Sample contained six drugs
am r p y ne norma ze y n erna
standard from DBS samples. Calibration
curve and %RSD variability (n=3) shown.
the [M+H]
+
ion of amitriptyline at
various concentrations from DBS
samples. Acquired at 70,000 resolving
power.
Mass accuracy 2-3 ppm
Amitriptyline
Y= -0.0519284+0.001756*X R^2=0.9933 W:1/X
9
1
787
40
60
80
100
304.1552
40
60
80
100
318.1710
ne
cocaethylene
cocaine
50
100
0
50
100
278.1911
278.1910
5000 ng/mL
1000 ng/mL
3
4
5
6
7
8
AreaRatio
300.2024
1
790
60
80
100
bundance
0
20
304.1910
304.1458
304.1646
304.1552
60
80
100
bundance
0
20
318.1918
318.1405
318.2283
318.1708
100
0
50
100
0
278.1910
278.1909
500 ng/mL
250 ng/mL
0
1000
2000
3000
4000
5000
ng/mL
0
1
2
300.2024
7
60
80
100
0
20
40
Relative A
304.1973
304.1760
304.1552
60
80
100
0
20
40
Relative A
318.1403
318.1919
318.1708
100
0
50
100
0
50
278.1910
278.2183
278.1909
100 ng/mL
50 ng/mL
Level (ng/mL)
% RSD
300.2024
1
60
80
100
0
20
40
304.1891
304.1377
304.1551
60
80
100
0
20
40
318.1404
318.1919
318.1708
318.1402
100
0
50
100
0
50
278.2180
278.1911
278.2182
278.1909
278 2180
25 ng/mL
10 ng/mL
Conclusion
300.20
300.1870
304.15
304.20
m/z
0
20
40
304.1763
304.1373
318.1
318.2
m/z
0
20
40
318.2284
318.1919
278.15
278.20
m/z
0
50
.
• We have shown an easy to use technique (no sample preparation, no chromatography)
that shows extraordinary potential for the semi-quantitative screening of drugs of abuse in
forensic toxicology.
esolving power of 140,000
tive detection. An enhanced
0 resolving power, data not
or and fragments (4-5 ppm
tion of compounds in
• Any combination of user required experiments,
e.g.
, MS, AIF and Data Dependent
MS/MS, are allowed for the best hit confirmation in a single experiment.
• Accurate mass fragments (from AIF or DD MS/MS experiment) and isotopic pattern
ur shown below.
etamine
119.0859
150 1280
NL: 1.78E7
matching are required to confirm drugs identified solely by accurate mass (Fig. 3).
• We have demonstrated feasibility for rapid blood analysis for intoxication cases where
expected concentrations are high (≥100 ng/mL, Fig. 4). DD MS
2
data (Fig. 5) indicates
1000 ng/mL
.
119.0859
150.1280
NL: 9.06E6
lower levels can be achieved and this is part of ongoing investigations.
• High resolution and accurate mass are crucial techniques for analyzing complex samples
by MS and nicely complement the paper spray technique in the screening of drugs from
d i d bl
d t
500 ng/mL
120
140
149.0237
119.0858
NL: 1.59E6
r e oo spo s.
• Data collected in this screening application allows for retrospective analysis as a full scan
MS event is always acquired.
100 ng/mL
196.1336
NL: 6.90E7
• The paper spray technique coupled with automated data processing using TraceFinder
3.0 software provides a complete solution for drug screening in forensic toxicology.
ne
References
1000 ng/mL
0917
318.1704
196.1336
0917
NL: 3.74E7
1. Manicke, N.; Yang, Q.; Wang, H.; Oradu, S.; Ouyang, Z.; Cooks, R.G. Assessment of
Paper Spray Ionization for Quantitation of Pharmaceuticals in Blood Spots.
IJMS
2011
,
300
, 123-129.
500 ng/mL
318.1705
196.1336
0917
318.1704
NL: 6.60E6
For forensic toxicology use only.
All trademarks are the property of Thermo Fisher Scientific and its subsidiaries.
This information is not intended to encourage use of these products in any manners that might infringe the
intellectual property rights of others
100 ng/mL
0 200 250 300
.
PO64316-EN 1114S



















