
A Complete Toxicology Screening Procedure for
Drugs and Toxic Compounds in Urine and
Plasma Using LC-MS/MS
Marta Kozak, Taha Rezai, Thermo Fisher Scientific, San Jose, CA
Key Words
• ToxSpec
Analyzer
• ToxID Software
• LXQ Linear Ion
Trap
• Clinical
Toxicology
• General
Unknown
Screening
Application
Note: 449
Introduction
Toxicology laboratories commonly use automated
immunoassays, gas chromatography-mass spectrometry
(GC-MS) and high pressure liquid chromatography-diode
array detector (HPLC-DAD) techniques to perform
toxicology screening analyses. None of these techniques
are able to identify all the drugs and toxic compounds
that are potentially present in a sample. Implementation of
liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) for
toxicology screening provides specific and sensitive
analysis of drugs and toxic substances. The benefits of the
LC-MS/MS screening methodology include a simple
sample preparation procedure, ease of adding new
compounds to the screening method and fewer limitations
based on compound volatility and thermal stability. In
addition, Thermo Scientific ToxID automated toxicology
screening software is able to automatically generate both
Summary and Long Reports, avoiding the need for
manual analysis of each sample chromatogram. This
application note describes the use of the Thermo Scientific
LXQ ion trap mass spectrometer equipped with an ESI
source and HPLC for identification of unknown
compounds in human urine and human plasma.
Goal
To develop a complete LC-MS/MS screening methodology
which includes a sample preparation method, LC-MS
method, spectra library, and data processing and reporting
software.
Experimental Conditions
An MS/MS spectral library of 275 drugs and toxic
compounds was created. Sample preparation of spiked
human urine or human plasma was carried out using a
solid-phase extraction (SPE) cartridge for basic, neutral
and acidic compounds. A 13-minute LC method
implementing a Perfluorophenyl (PFP) column was
developed. Samples were analyzed using electrospray
ionization (ESI) on an ion trap mass spectrometer in
polarity switching scan dependent MS/MS experiments
(see Figure 1), with retention time windows specified for
each listed parent mass. The method allows acquisition of
MS
2
spectra for co-eluting compounds and analysis of
positively and negatively ionized compounds with a single
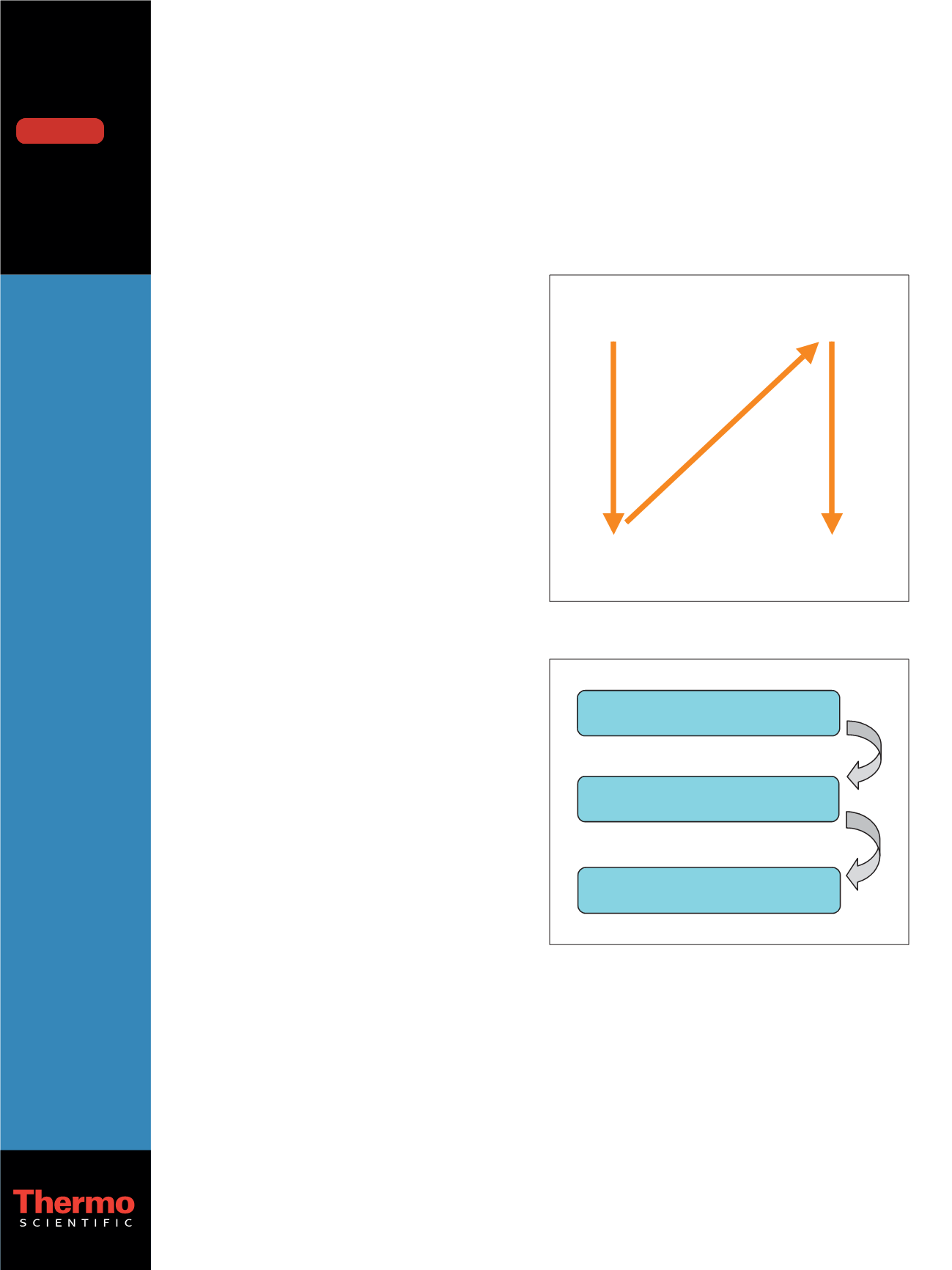
run. Figure 2 shows the overall application workflow.
Scan Event 1
+ Full Scan MS
Scan Event 2-6
+ MS/MS on parent list
Scan Event 7
– Full Scan MS
Scan Event 8-9
– MS/MS on parent list
Figure 1: MS scan events
Step 1: Extract analytes from urine
or plasma with SPE procedure
Step 2: Analyze the samples
with LC-MS/MS method
Step 3: Automated library search and
reporting with software
Figure 2: Step-by-step application workflow
Sample Preparation
Samples (1 mL of urine or 0.5 mL of plasma) were spiked
with 0.1 mL of an internal standard solution at a
concentration of 1 µg/mL (Chlorpromazine-D3,
Haloperidol-D4 and Prazepam-D5) and diluted with 2 mL
of 0.1 M phosphate buffer pH 6.0. The resulting mix was
extracted with an SPE (Thermo Scientific Hypersep Verify-
CX 200 mg mixed mode cartridges) procedure prior to
injection onto LC-MS.



















