
Fast and Accurate Determination of
Algal Toxins in Water Using Online
Preconcentration and UHPLC-Orbitrap
Mass Spectrometry
Jaewon Choi,
1
Je-Heon Jang,
1
Jennifer Massi,
2
Jonathan Beck
2
1
Water Analysis & Research Center, K water, Daejeon 306-711, Korea
2
Thermo Fisher Scientific, San Jose, CA, USA
Application Note 606
Key Words
EQuan, Exactive, Orbitrap, algal toxins, cyanobacteria, water analysis,
online concentration
Goal
To develop a column-switching technique based on online preconcentration
and high-resolution, full-scan
Thermo Scientific ™ Orbitrap ™ mass
spectrometry to obtain fast and accurate results for the determination of
algal toxins in drinking water.
Introduction
When the density of the colonies of
Microcystis
and
Nodularia
cyanobacteria surpass a certain level, they
produce hepatotoxic substances called microcystins and
nodularins, respectively,
2
while
Anabaena
and
Apha-
zinomenon
are known to produce a neurotoxin called
anatoxin.
3
These toxins can cause deaths of wild animals
and domestic livestock. Human poisoning can lead to
gastrointestinal and allergy-like reactions and, in rare
occasions, death. Of the cyanobacteria species,
Microcystis
has been observed to be dominant in the majority of
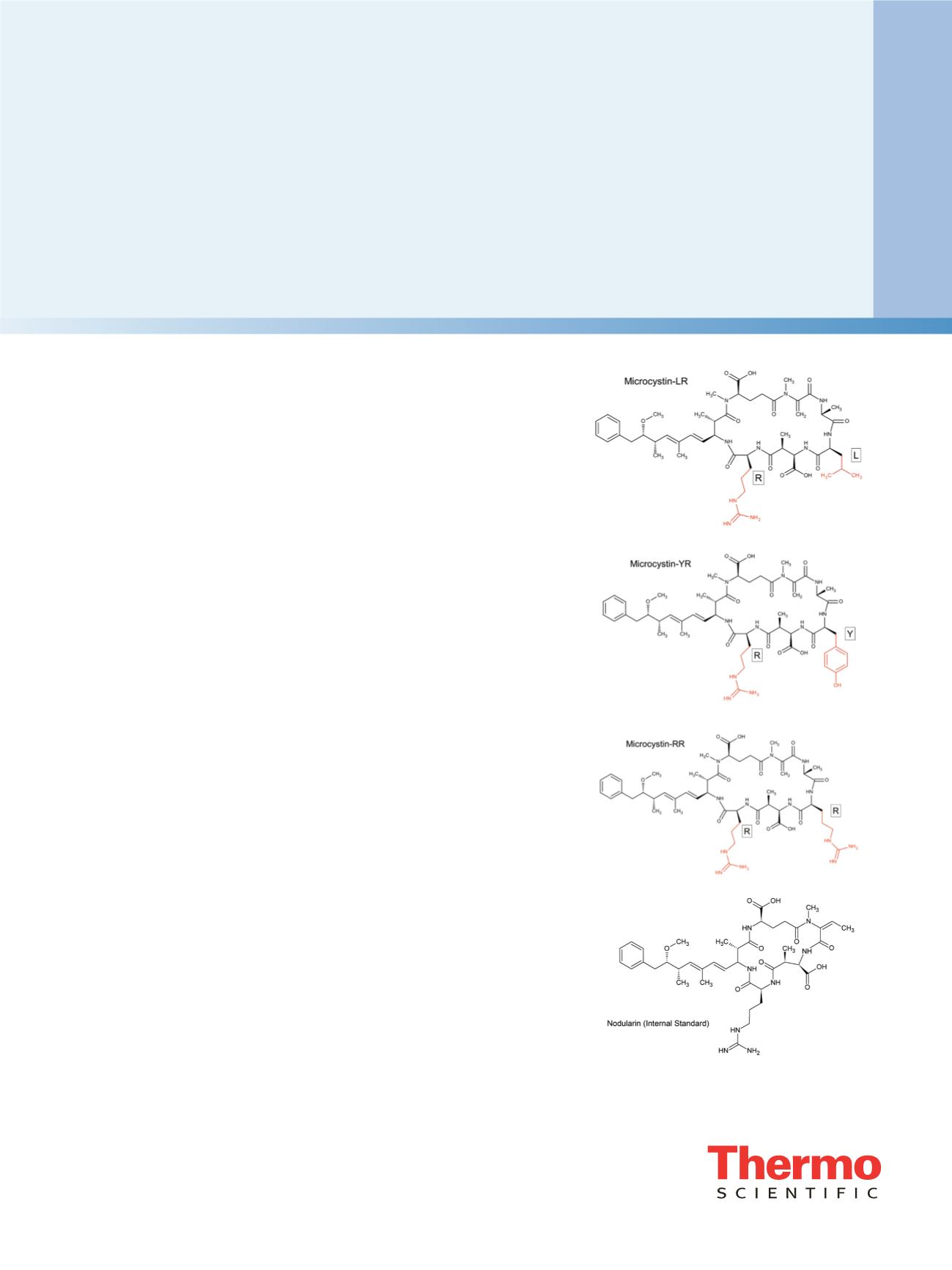
eutrophication events. Microcystins, the toxins it
produces, are cyclic peptides comprised of seven amino
acids, each with a relatively large molecular mass ranging
from 900 to 1,100 Da. There are approximately 60 to 85
variants of microcystins reported to date (Figure 1).
4,5
Moreover, nodularins produced by
Nodulariais
are
peptide-based hepatotoxins similar to microcystins.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO),
microcystins are chemically stable and can have an
adverse impact on human health if present in a water
supply source.
1
Prior research has shown that the
microcystins -YR, -RR, and -LR (Figure 1) are the most
common isomers detected, and that microcystin-LR is the
most toxic. Based on these results, the WHO has set forth
a water quality guideline specifying that the microcystin-LR
concentration be maintained below 1 ng/mL. This
guideline is currently being used in Korea as part of a
candidate list for drinking water standards.
Figure 1. Structures of the cyclic peptide microcystins and
nodularin



















