
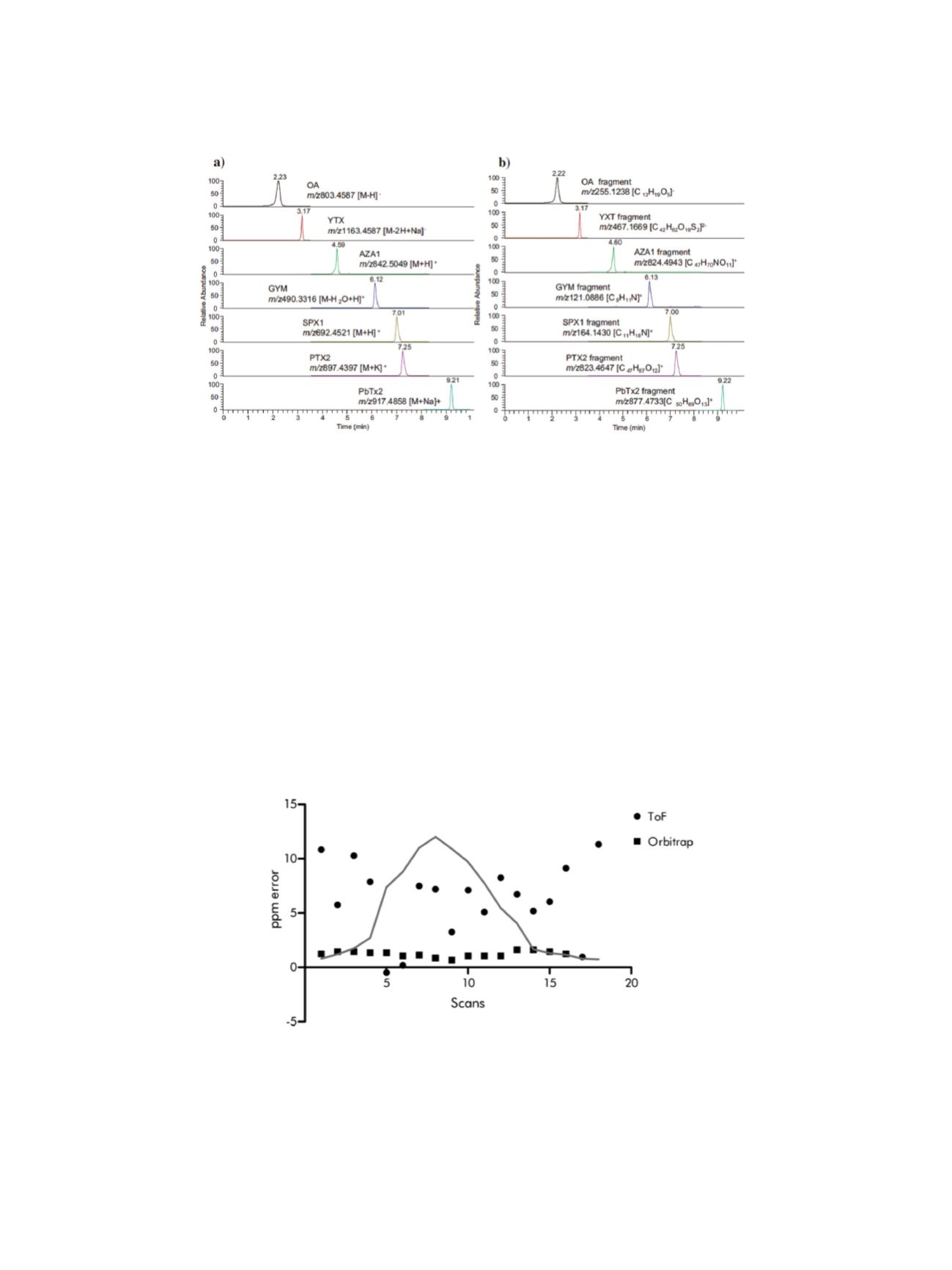
5
As documented in Figure 3, obtaining both precursor and fragment ion chromatograms allowed
scientists to provide enough confirmatory information to comply with EU analytical method
quality criteria.
9
Additionally, during the study, researchers performed complete validation of the
method and documented excellent performance in routine quantitative analysis.
Figure 3. Extracted ion chromatogram of the lipophilic marine toxins, showing (a) diagnostic ions and (b) fragment ions, with an
extraction window of 5 ppm..
However, the scope of the HRAM approach reaches far beyond the details discussed above. The
acquisition of accurate mass spectra (MS and MS/MS) enables the creation of libraries that could
be used for comprehensive toxin screening. As described in the work of Gerssen et al, the data
obtained by the Thermo Scientific
™
LTQ Orbitrap XL
™
hybrid ion trap-Orbitrap mass spectrometer
were processed and corresponding spectra were created.
10
The library contains information about
compound name, accurate mass, mass deviation (<5 ppm), retention time (min) and retention time
deviation (<0.2 min). Gerssen also documented a superior level of precision provided by the
Orbitrap MS compared to a TOF technique when screening for compounds by using accurate mass.
As can be seen in Figure 4, mass error deviation is almost an order of magnitude lower when the
Orbitrap MS is used. This drastic difference in results is related to the fact that, when screening for
compounds by using accurate mass, usually a data extraction window of +/– 5 ppm is used. High
errors observed in TOF data don’t usually allow the application of such a narrow window, which
subsequently negatively influences selectivity of TOF instruments.
Figure 4. Mass error observed within a chromatographic peak of AZA1 recorded by Time-of-Flight (ToF) and Orbitrap MS.
Reprinted with permission from: Giessen
et al.
Analytica Chimica Act 685 (2011) 176–185.



















