
Analysis of Perfluoroalkyl Acids in Wastewater,
Sludge, and Liver Extracts Using High-
Resolution, Accurate Mass LC-MS
Frans Schoutsen
1
, Helen Welchman
2
, Rossana Bossi
3
;
1
Thermo Fisher Scientific, Breda, The Netherlands;
2
Thermo Fisher Scientific, Hemel Hempstead, United Kingdom;
3
Aarhus University, Roskilde, Denmark
Application
Note: 543
Key Words
• Exactive
• Orbitrap
technology
• Environmental
application
• PFAAs
• PFOS
Introduction
Perfluoroalkyl acids (PFAAs) are global pollutants and
have been shown to bioaccumulate in the food chain.
PFAAs have been detected in livers of fish, birds, and
marine mammals from Greenland and the Faroe Islands.
1
Biomagnification of perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS), the
predominant fluorochemical detected, was observed along
the marine food chain (Figure 1).
The performance of the Thermo Scientific Exactive
mass spectrometer equipped with Orbitrap™ technology
has been evaluated for the analysis of ten selected
perfluoroalkyl acids in pooled extracts from environmental
samples. The following PFAAs were analyzed:
perfluoroheptanoic acid (PFHpA), perfluorooctanoic
acid (PFOA), perfluorononanoic acid (PFNA),
perfluorodecanoic acid (PFDA), perfluoroundecanoic
acid (PFUnA), perfluorododecanoic acid (PFDoA),
perfluorotridecanoate acid (PFTrA), perfluorohexane
sulfonate (PFHxS), perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) and
perfluorooctane sulfonamide (PFOSA) (Figure 2).
The sample extracts were chosen to represent both
high and low levels of the analytes in complex matrices.
Low levels were expected in liver extracts from Antarctic
seals. Medium and high levels were expected in Arctic
seals, influent water, and sludge from a wastewater
treatment plant. The performance has been evaluated in
terms of linearity (range 0.1-50 µg/kg), specificity, and
sensitivity.
Goal
To demonstrate the performance of the Exactive™ high-
resolution, accurate mass benchtop liquid chromatogra-
phy-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) system in the analysis of
ten selected perfluoroalkyl acids.
Experimental Conditions
Sample Preparation
The sample preparation process is illustrated in Figure 3.
Liver samples were extracted by ion pairing with tetrabu-
tylammonium hydrogen sulfate (TBAS) and methyl tertiary
butyl ether (MTBE). Sludge samples were extracted by
sonication with methanol followed by solid phase extrac-
tion (SPE). Effluent water samples were extracted by SPE
on C18 columns.
HPLC
Chromatographic analysis was performed using a Thermo
Scientific Accela autosampler and pump. The chromatog-
raphy conditions were as follows:
HPLC column:
Thermo Scientific Hypersil GOLD,
50 mm x 2.1 mm, 1.9 µm
Pre-column:
Thermo Scientific Hypercarb, 100 mm x 2.1 mm, 5 µm
Column temperature: 40 ºC
Mobile phase C:
Ammonium acetate (2 mM)
Mobile phase D:
90% water, 10% ammonium acetate
A trapping column placed in line with the Accela™
pump and autosampler enabled less contamination of
perfluorinated compounds (PFC) into the system, thus
achieving a lower background.
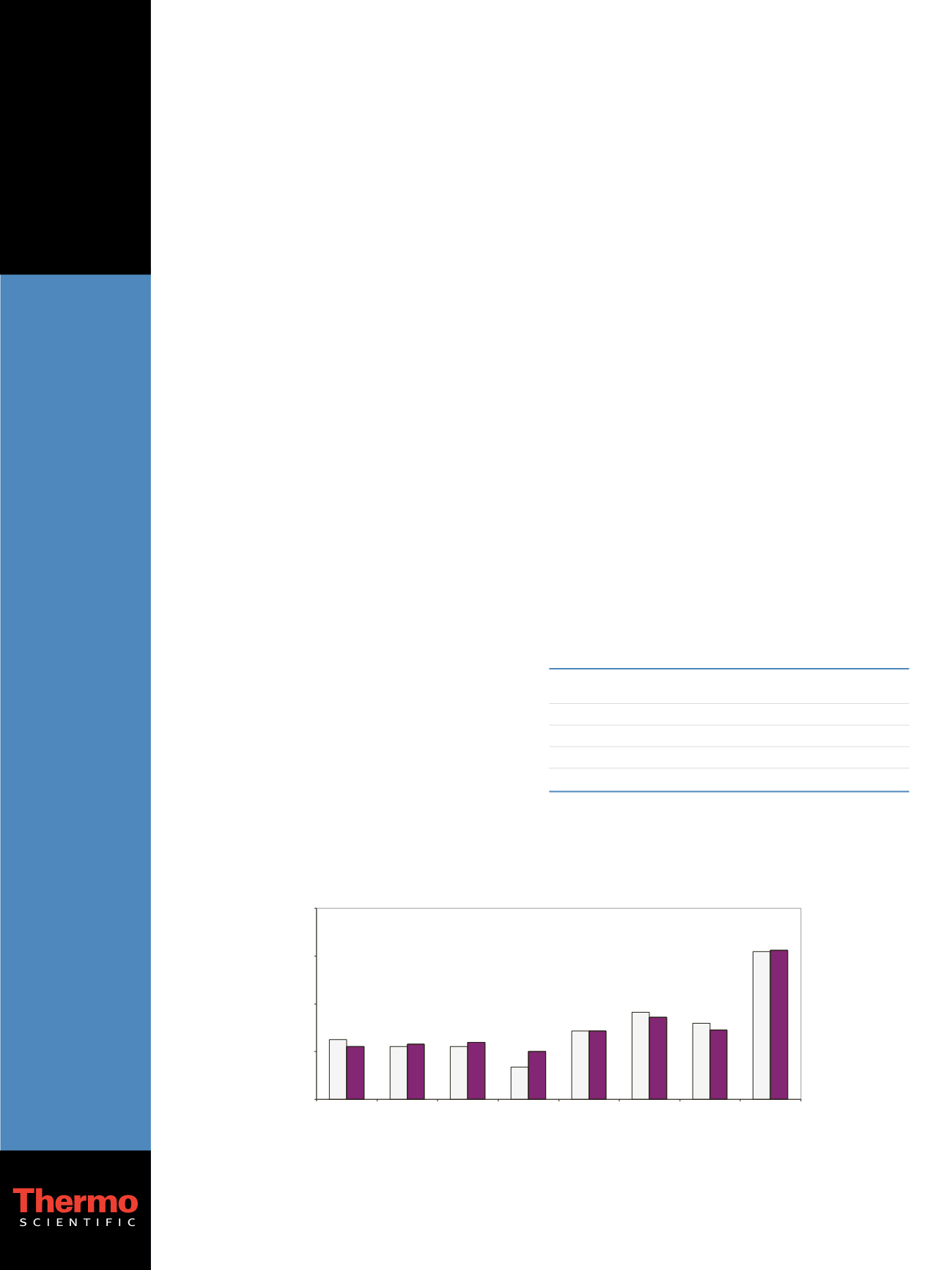
Figure 1. PFOS concentration in Arctic mammals, birds, and fish [Bossi et al. (2005)]
1
10
100
1000
10000
Shorthorn Sculpin
East Greenland
Black Guillemot
West Greenland
Black Guillemot
East Greenland
Ringed Seal
Central West
Greenland
Ringed Seal
Northwest
Greenland
Ringed Seal
East Greenland
Long Finned Whale
Faroe Islands
Polar Bears
East Greenland
PFOS (ng/g wet weight)
Figure 1. PFOS concentrations (analysis of two samples) in Arctic mammals, birds, and fish [Bossi et al. (2005)]



















