
3
Mass Spectrometry
Detection of analytes was performed on a Thermo Scientific
™
TSQ Quantum Access
™
triple-stage quadrupole mass
spectrometer equipped with a Thermo Scientific
™
Ion
Max
™
API source with an APPI probe.
Hydrocarbons (PAHs) are difficult to ionize by
conventional LC/MS techniques and yield poor response.
Using a dopant-assisted atmospheric pressure photo-
ionization (APPI) interface, an intermediary compound
was introduced at high concentrations into the APPI
source. This produced large numbers of ions, which in
turn underwent a kinetically favored charge transfer with
the eluting analytes, provided substantial sensitivity gain
relative to dopant-free photoionization.
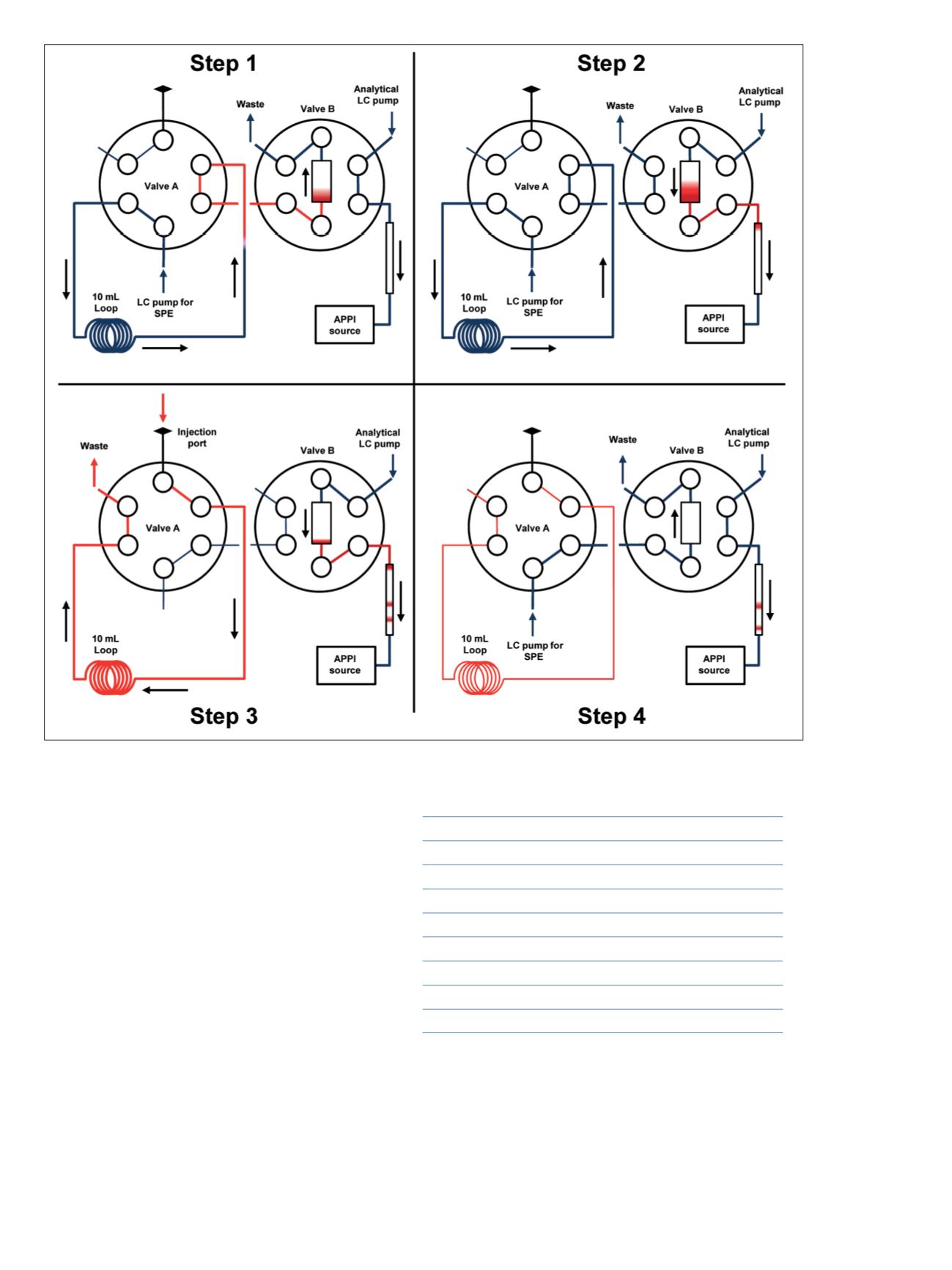
Figure 1. Online SPE system and automated analysis steps. Active flows are shown by arrows and thicker lines. Red: sample and PAHs;
blue: mobile phases
The following parameters were used for all analytes:
Ion mode
Positive
Skimmer offset
−10 V
Sheath gas (N
2
)
40 arbitrary units
Auxiliary gas (N
2
)
20 arbitrary units
Capillary temperature
250 °C
Vaporizer temperature
250 °C
Collision gas (Ar) pressure
2.1 mTorr
Scan time
0.020 s
Scan width
0.020
m/z
To reduce unnecessary instrument scans, two detection
segments were used (segment 1, 8–18 min, and segment 2,
18–28 min). Chlorobenzene dopant was introduced to the
APPI source only during the detection period (8–28 min)
through the nitrogen auxiliary gas line, delivered by two
programmable syringe pumps operating simultaneously for
total flow rate of 10% of that of the column eluent.
Selected-reaction monitoring (SRM) scan events were
obtained by direct infusion of individual PAH solutions
and are listed in Table 1.



















