15
Introduction
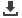
Solvent Selection in SPE
The choice of solvent is dependent
upon the sample matrix and the
retention mechanism used. The table
shows the differing polarities of
solvents commonly used in SPE.
Method Development Optimization in SPE
The use of SPE as a sample preparation technique can
significantly reduce the effects of ion suppression. For highest
recovery levels and cleaner extracts, optimization of the SPE
process is important. By optimizing the load, wash, and
elution steps of the SPE process, a cleaner sample extract can
be obtained, leading to benefits for the detection and robustness
of the analytical instruments. A gradual elution of the
compound from the cartridge results in the optimum wash
and elution conditions.
A range of drugs were investigated for different
HyperSep SPE phases. It was anticipated that the nature
of the drug, and the pH, would determine the optimum
conditions in which to perform the experiments. Of particular
interest is the effect of the elution conditions, as these
typically default to 100% organic, and this is not always
optimal for selective extraction of an analyte.
Factors that influence levels of recovery are:
•
pH levels
– Sample loading
– Buffers used
– Elution
•
Wash solvents
– Must not recover analytes
•
Elution solvents
– Polarity
– Solubility
– Elutropic strength
Application Examples
1) Optimization of Load Step
For Reversed-Phase Interactions
•
Neutral compounds are not affected by pH (no need to
adjust the pH of the sample)
•
For charged compounds, use at a pH at which the compound
is not charged. Neutralize the molecule according to the
following:
– For basic compounds, the neutral molecule exists at least
2 pH units below the pKa of the compound
– For acidic compounds, the neutral molecule exists at least
2 pH units above the pKa of the compound
For Normal-Phase Interactions
•
pH is not normally an issue in normal phase interactions,
as the solvents used are typically non-polar organic solvents,
rather than water.
•
There is no need to verify the sample application pH
For Ion-Exchange Interactions
•
pH and pKa are important considerations
•
Acidic compounds are extracted from a sample solution at
least 2 pH units above the pKa of the analyte
•
Basic compounds are extracted from a sample solution
2 or more pH units below the pKa of the analyte